Disclaimer
I am in no way telling you to go out and eat Gyromitra, but, like it or not, they are a traditional food eaten to this day in some places.
As people continue to eat them, with poisonings still occurring regularly from improper cooking, I've tried to present relevant details on these mushrooms and, most importantly, a tried and true method for cooking them that can help those who choose to eat Gyromitra each year, regardless of conflicting information on their edibility, not get themselves or others sick.

Original text
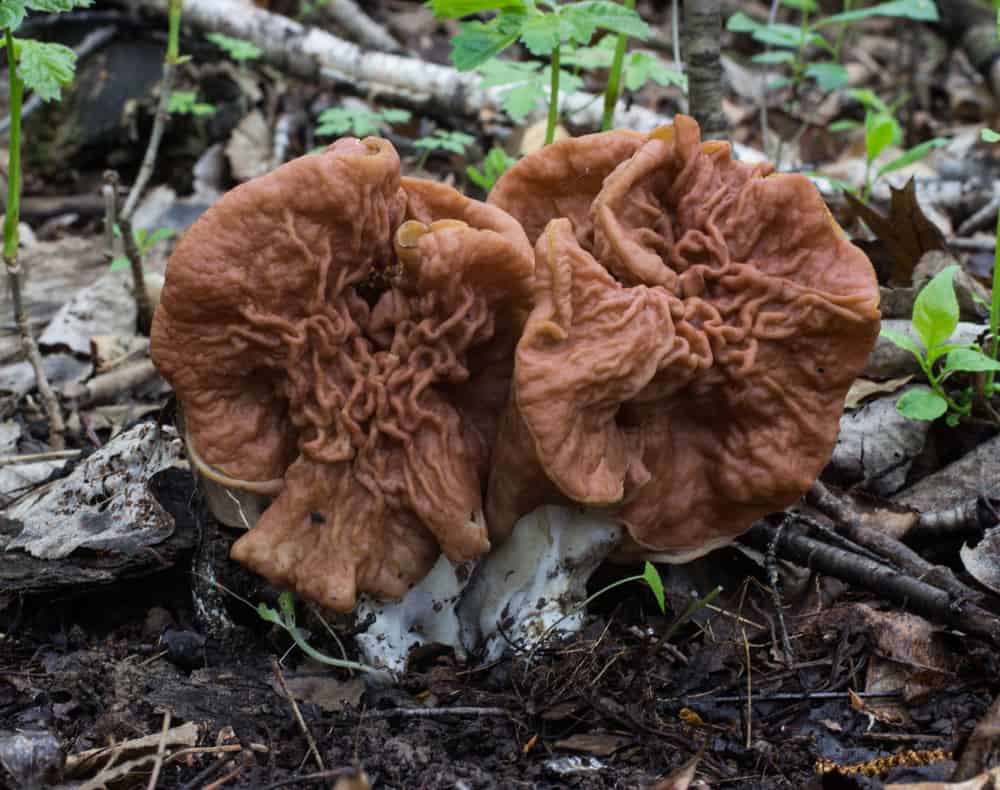
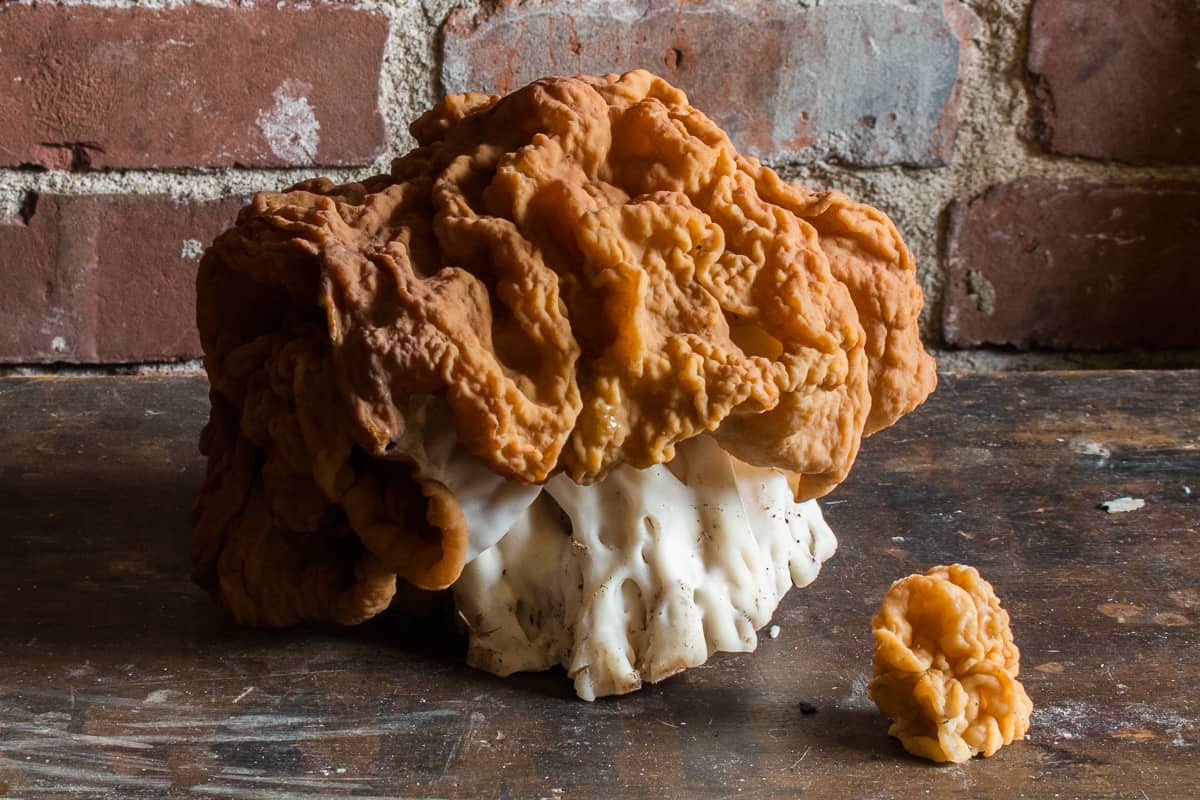
Behold Gyromitra, the false morel, scourge the mushroom hunters and terror of Spring!
I can still remember the first time I saw one, I felt insulted. I knew they were deadly from seeing a picture of them with a skull and crossbones in a guide, even seeing them was scary.
I looked at them like some sort of desecration of my morel patch, an abomination. I remember stomping on all of them with angry fear, damn right I was going to destroy every single one of them. I was even uneasy cleaning them out of the soles of my boots.
Later that year I saw something strange after I'd put up a couple posts on poisonous mushrooms to help round out the collection of basic ID posts on mushrooms I've done for this site.
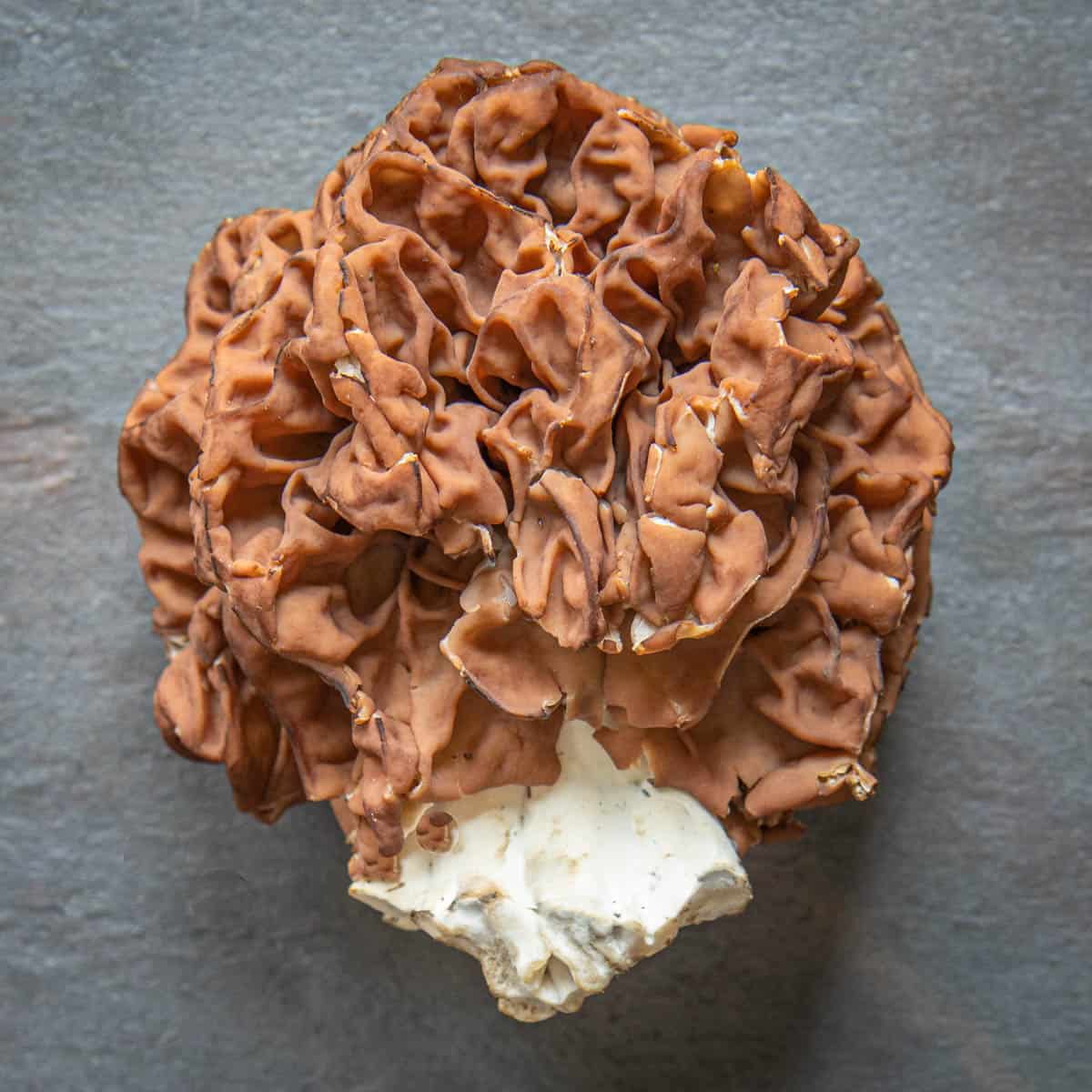

The first post I put up was a basic one on Gyromitra, the family of mushrooms known casually as false morels, death verpas, false peckerheads, beefsteak mushrooms, brain fungus, reds, etc, with a couple pictures and paragraphs.
I would expect the post to get more traffic during morel season, which it did, but when I looked at keywords people were using that led them to the site I was shocked, there were a number of combinations like the following:
- "False morel, how to eat/cook"
- "Best way to eat false morel, beefsteak mushroom"
- "Cooking/eating brain fungus mushroom"
- "Best false morel recipe"
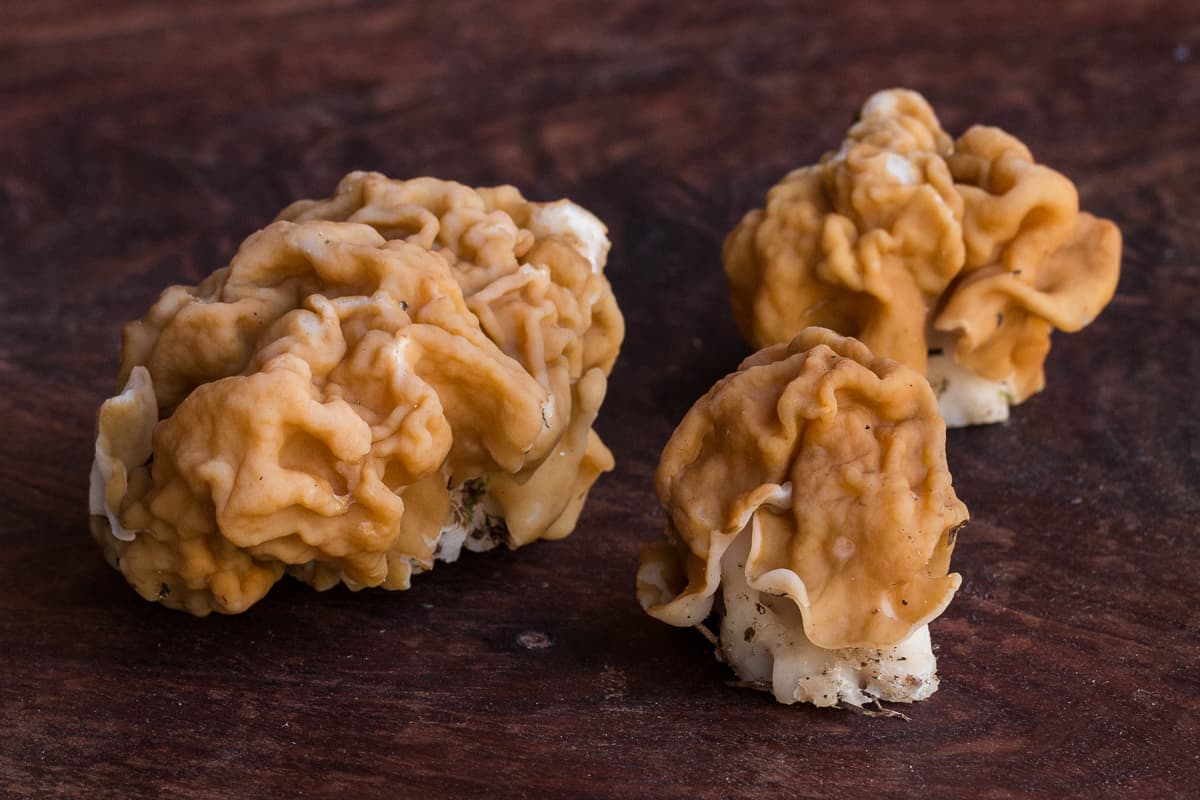

People have eaten false morels around the world, for a long time
Even a few searches for eating a poisonous mushroom would be a little odd, but the kicker was the geographic density of the searches. The vast majority of the searches for cooking Gyromitra were coming from different parts of Michigan, and most of them on the Upper Peninsula. Now I was curious.
I didn't understand, shouldn't they all be dead? What was going on?
About this time, I lost myself hunting morels and forgot about the Gyromitra for a couple years, until I had a conversation with my friend Patrick, the most experienced mushroom hunter I know, and a well connected member of our local mycological society.
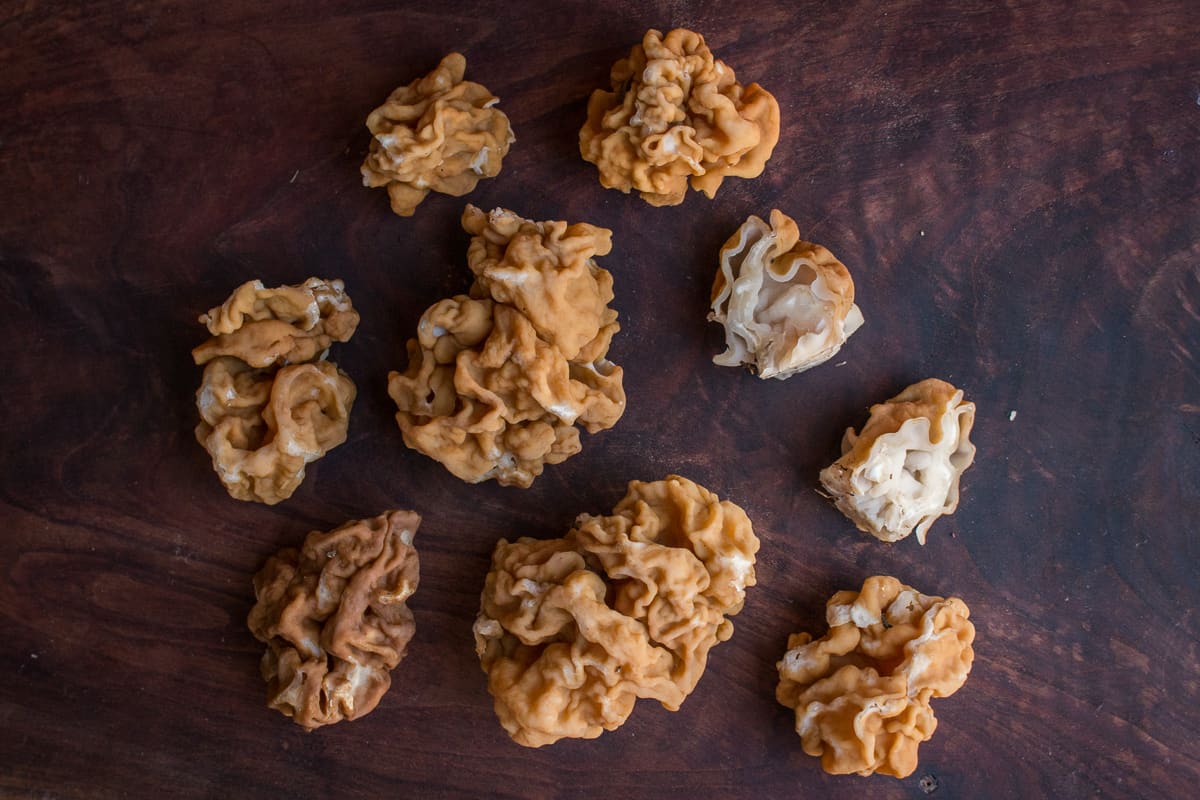

Consumption in Europe
He told me the story of a friend, an old doctor of Finnish descent, and the family doctor to his wife during her childhood. The doctor, like a lot of people close to their European ancestry, loves hunting his mushrooms.
The doctor's favorite were Gyromitra. He'd told Patrick stories of markets in Finland where dried Gyromitra are piled up to the ceiling for sale, and to boot, Patrick's wife can remember dining on fried Gyromitra in her youth at the doctor's house with her family.
By Patrick's wager, the doctor has probably eaten the mushrooms every year for around 50 years, and similar stories are not hard to find doing a simple internet search.
Lorchel and Murklor
A little deeper search, using terms like Murklor (a Scandinavian catch-all term for Morchella, Verpa, and Gyromitra) will further illustrate historical consumption in Europe, and....they even used to be sold canned in Germany, where they're known as Lorchel. The problem, is that there's conflicting evidence to the tenability of being a long-term false morel eater.
The alleged problem is that Gyromitra contain a compound that gets metabolized into monomethylhydrazine in the body, which is a carcinogenic compound of rocket fuel that is both contained in the flesh of the mushroom, and apparently gets cast into the air during cooking.
This makes false morels the only mushroom I'd heard of that you could get sick from cooking, even if you don't eat them. As fascinating as the natural bio-synthesis of fuel components in mushroom form may be, they're probably not that good to have in your body.
This sounds pretty cut and clear, false morels are bad, obviously, I mean they're called "false morels", right? But, if these mushrooms are truly as deadly, dangerous, and as terrifying as we make them out to be is hotly debated in the mushroom community.


Amounts of Gyromitrin Can Vary Greatly Between Species
The danger seemed to be that the toxin gyromitrin from the mushrooms builds up in your body. To further confuse and compound things, different species of Gyromitra can have negligeable amounts of the toxin gyromitrin (see G. montana and G. caroliniana), or a lot (Gyromitra esculenta).
This accounts both for deaths involving eating the mushrooms, and for the anomaly of long time, habitual eaters like our friends in the Upper Peninsula. Now we're getting somewhere.

Identification
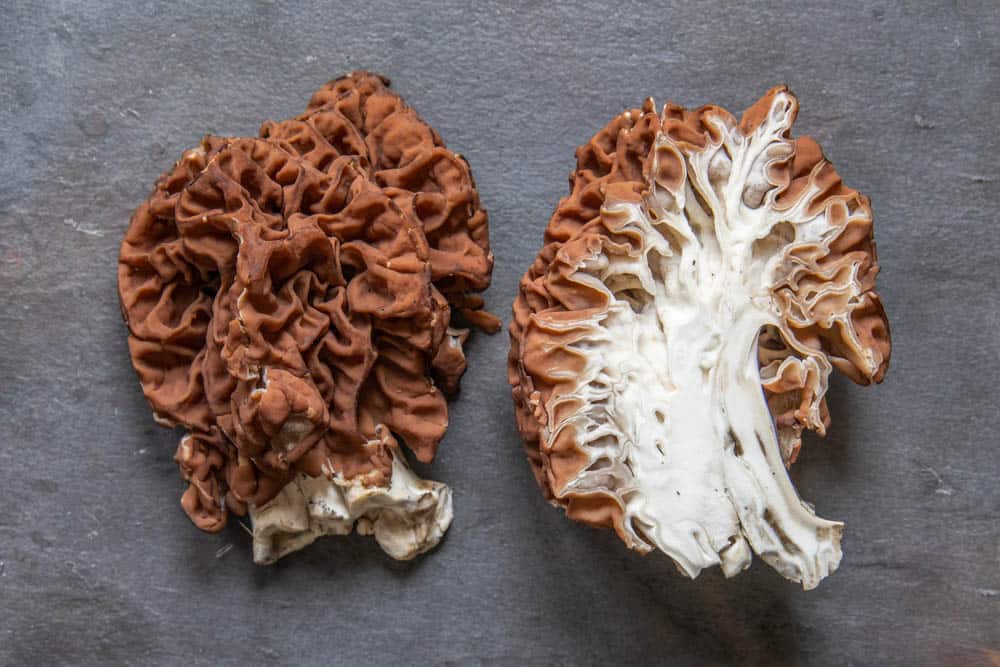
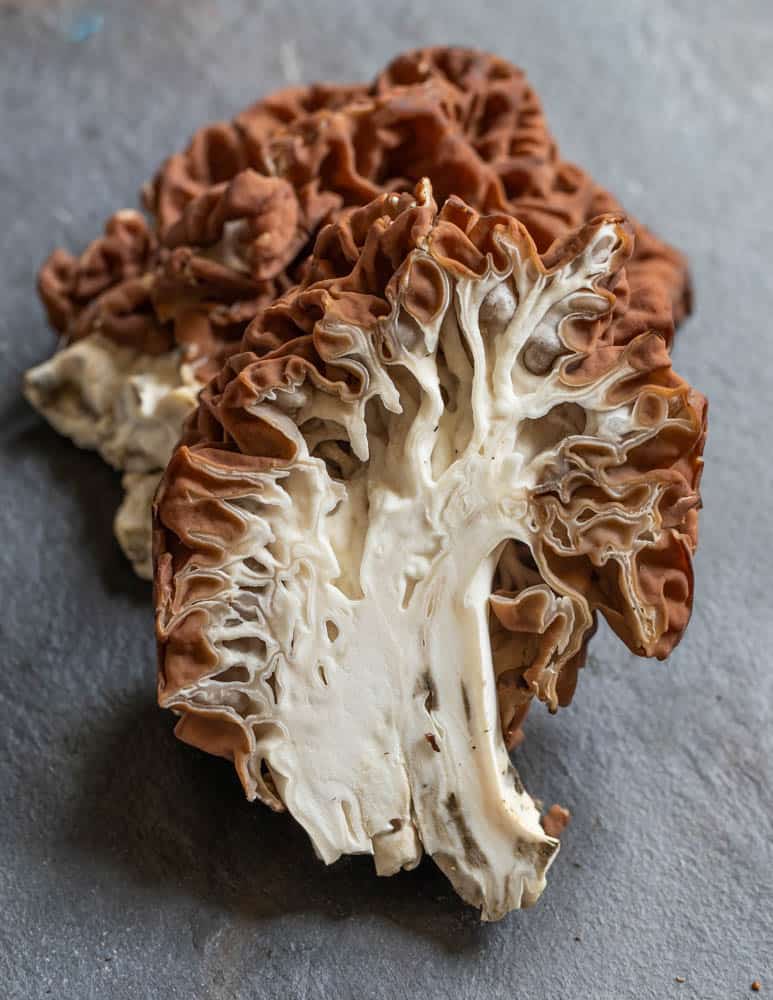
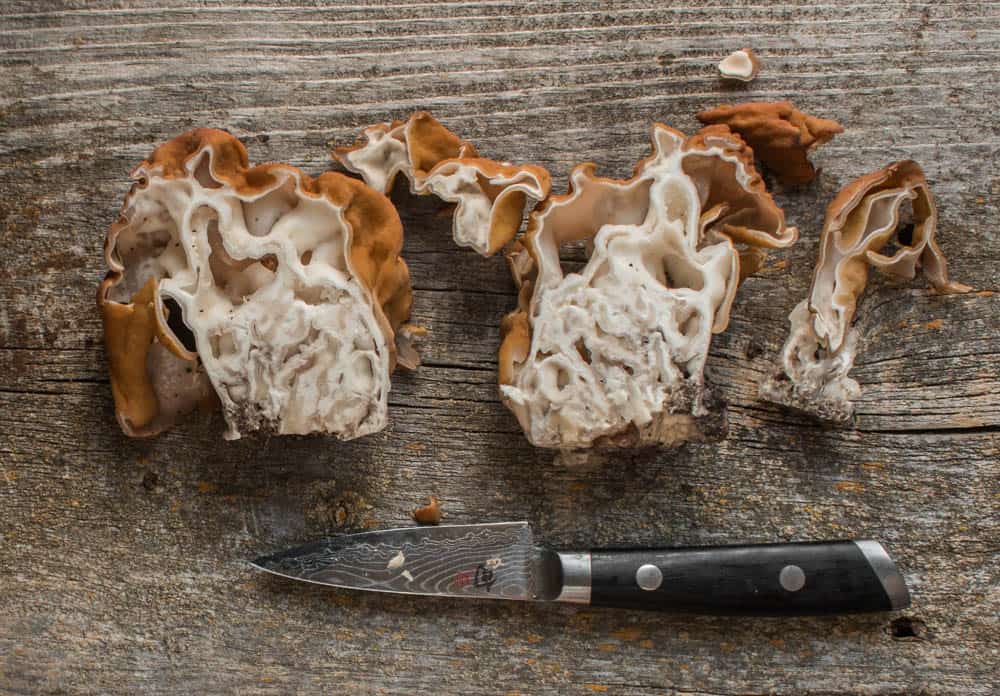
Gyromitra can look similar to morels for people just starting to hunt mushrooms, but there's two key points that will help you separate them in the field.
- Gyromitra have folds, not pits like morels in their caps.
- While morels are hollow, false morels are not, as you can see in the above picture.
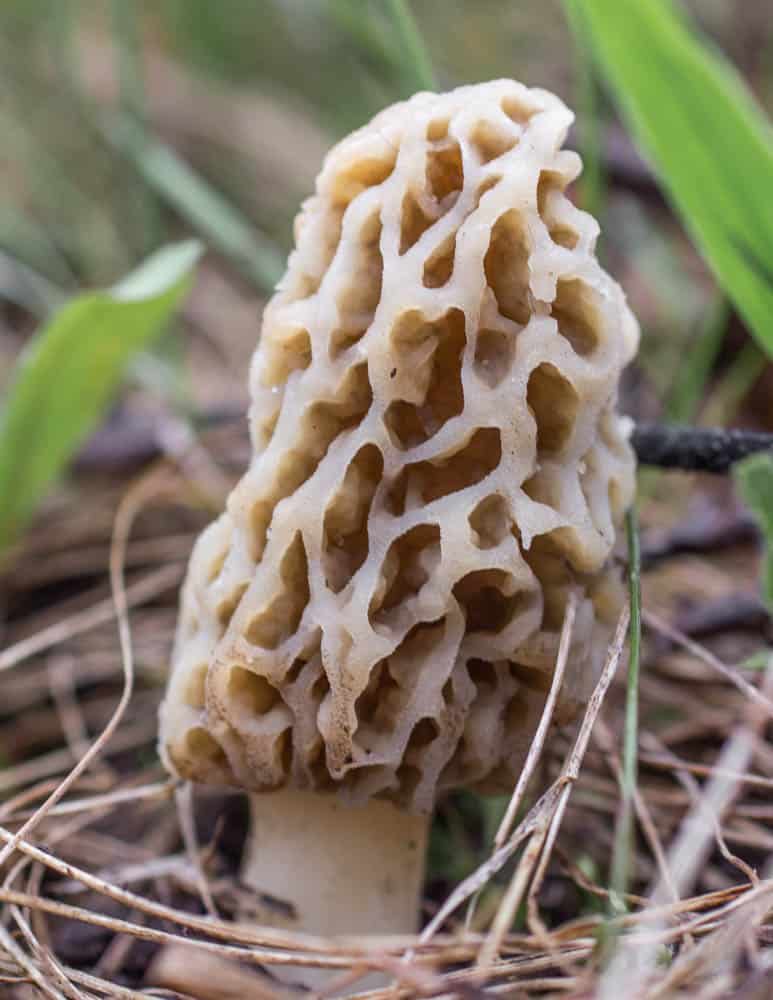
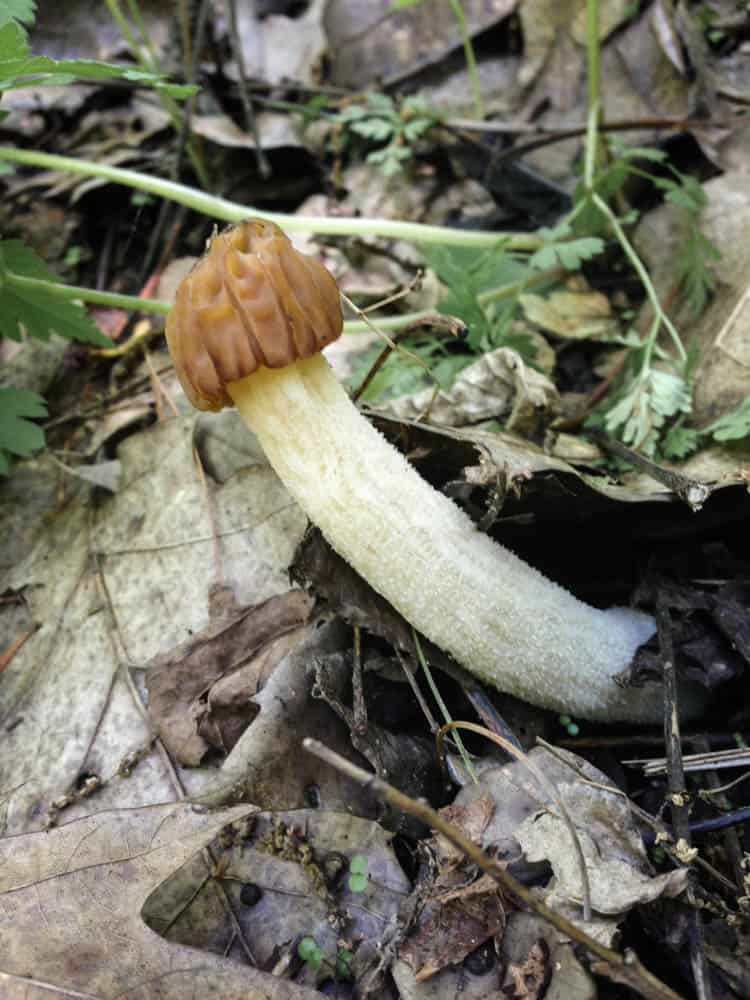
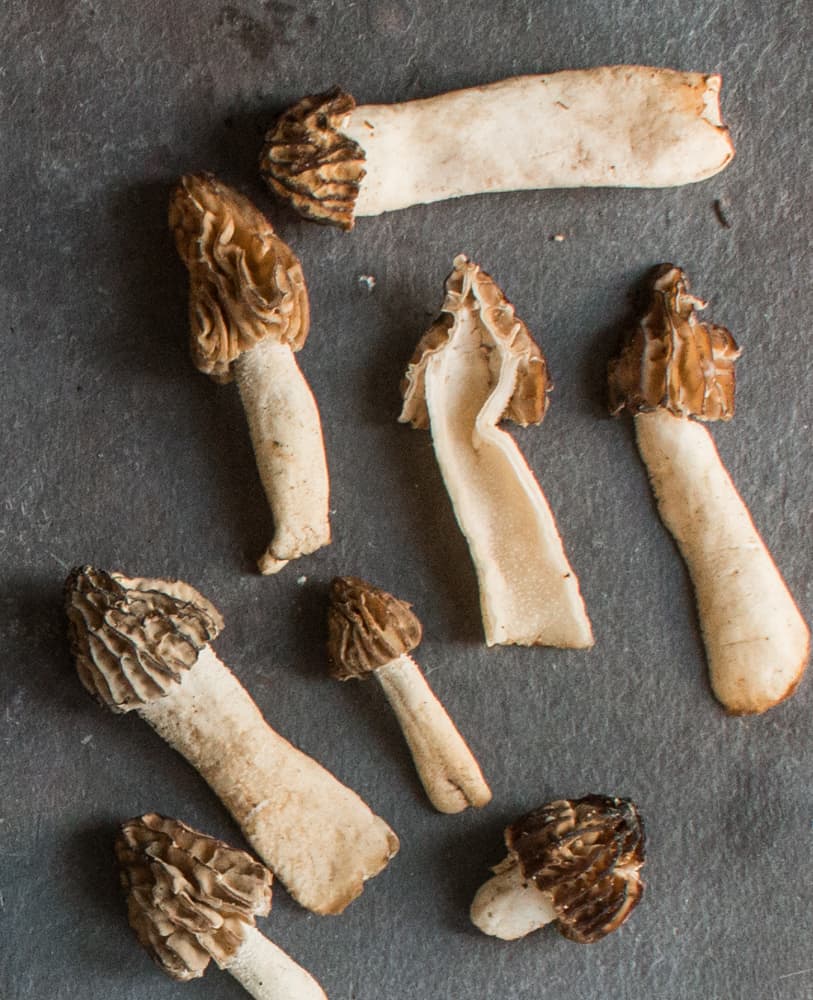




Morphology / shapes
There's a lot of variation with these mushrooms. Here's some really helpful images put together by Wes Lee, a member of False Morels Demystified.
See a link to the popular morel myth-busting Facebook group at the bottom of the post. I'd suggest copying the image below or saving to your phone to help with your identification.

Edibility
In an article for Fungi Magazine, Mycologist Michael P. Bueg writes the following synopsis regarding G. caroliniana and brunea (link to the whole article at the bottom of this post).
"I conclude that Gyromitra
caroliniana and Gyromitra brunnea
(the two species are easily confused)
are probably no more dangerous to
consume than Morchella species"
According to Bueg, Gyromitra are, at the same time, edible, delicious, and dangerous, but it all has to do with the exact species of Gyromitra being consumed. It appears that some Gyromitra could contain levels of gyromitrin so low they're completely edible, some, quite the opposite.
Thankfully a recent study came out with a new method for testing the levels of gyromitrin in specific species. The mushroom species in blue below had negligeable levels of gyromitrin, while the species in red (especially the Esculenta clade) do. Gyromitra species colored in blue can be sauteed / cooked (very well, at least 15 minutes) as you would cook morels. They can also be dried.
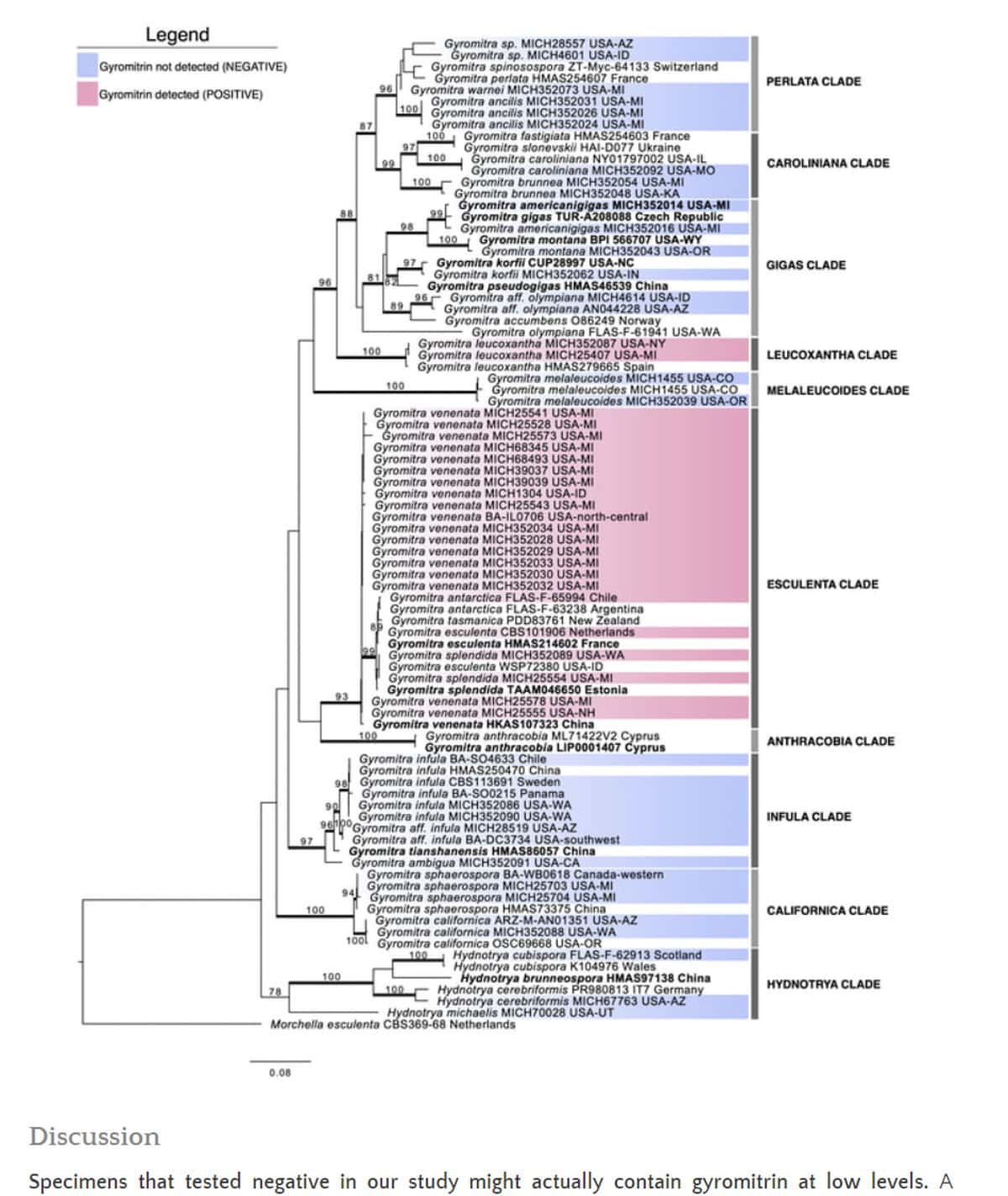

Gyromitra esculenta can be dangerous
For the most part, Gyromitra esculenta, if it isn't confusing enough having the last part of it's name as a word meaning edible, is reputed to be the most dangerous as far as the concentration of Gyromitrin/hydrazine, and this is confirmed by the Alden study.
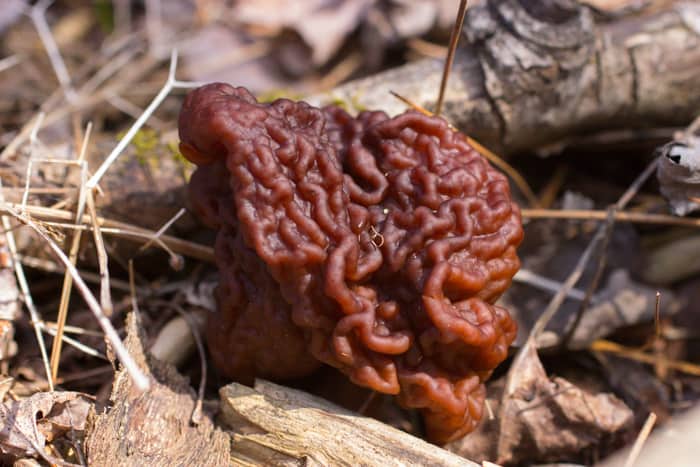

Even more confusing, is the fact that G. esculenta could possibly be the most widely consumed Gyromitra in the world, as countries that have historically eaten the mushroom are known for consuming the particular species.
While some Gyromitra experts will say, yes, all the gyromitra are edible, and some like Gyromitra caroliniana don't even need to be boiled before eating, all will agree G. esculenta always needs to be boiled if it's going to be eaten.
Personally, I'm probably only going to eat caroliniana, brunnea, and korfii, but when I do, it's in small quantities in the spring.

Cooking, Eating, and Safety
Taking all that into account, and going against just about every ounce of logic my brain had, I knew my curiosity wouldn't be sated until I tasted one, so I told my friend Alex, a local mushroom hunting savant to be on the look out for them.
A few days later she came around and I had myself some false morels, along with a few sarcastic jeers.
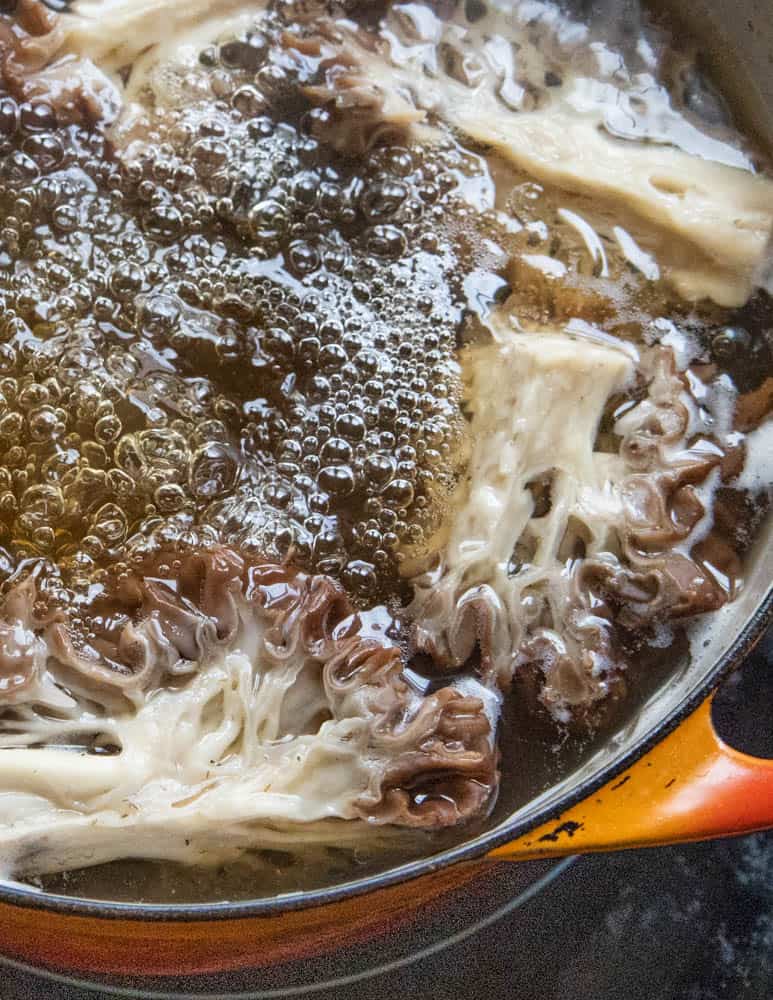
I waited until I had a day off, opened a window, turned on the fan and the hood vent, brought a pot of salted water to a boil with the mushroom, put a lid on top of the pot and tied a rag around my face for fear of the air-borne hydrazine killing or blinding me.
I went and sat down in the other room while the Gyromitra simmered away. After a few minutes I could start to smell something in the air, it smelled nice and mushroomy, but that was all.
My friend Patrick said that he had walked into the doctor's house while he was boiling Gyromitra and could smell the rocket fuel in the air, so I wanted to know if it was true, again, maybe the varying levels in mushrooms can smell different when cooked, I don't know.

After I could tell my little false morel was totally cooked through, I took it out of the pan, threw away the water, dried it thoroughly (very important since water gets trapped in the cavity of the false morels and will pop and explode in a hot pan), then I fried it in butter and ate it alone, in a dark corner, with a napkin on top of my head to hide my shame from god.
How do they taste?
Here's the thing about forbidden fruit, it isn't usually forbidden because it tastes bad. I would be lying if I said eating the Gyromitra didn't taste very good, these were like eating a giant morel, although milder from the par-boiling.
The folds inside the stem that are usually a hollow in morels catch and hold all sorts of juices, tasting like tender layers of morel-flavored ruffles. You might be wondering why I would describe how to cook a false morel, below-the answer brings us back to what lead me to these in the first place.
People will continue to eat false morels whether you, me or other mushroom hunters think they should or not.
As there's a lack of information on the subject I wanted to provide a template with precautions and clear directions people could find to reference, since they're one of the most common culprits of mushroom poisoning in North America.
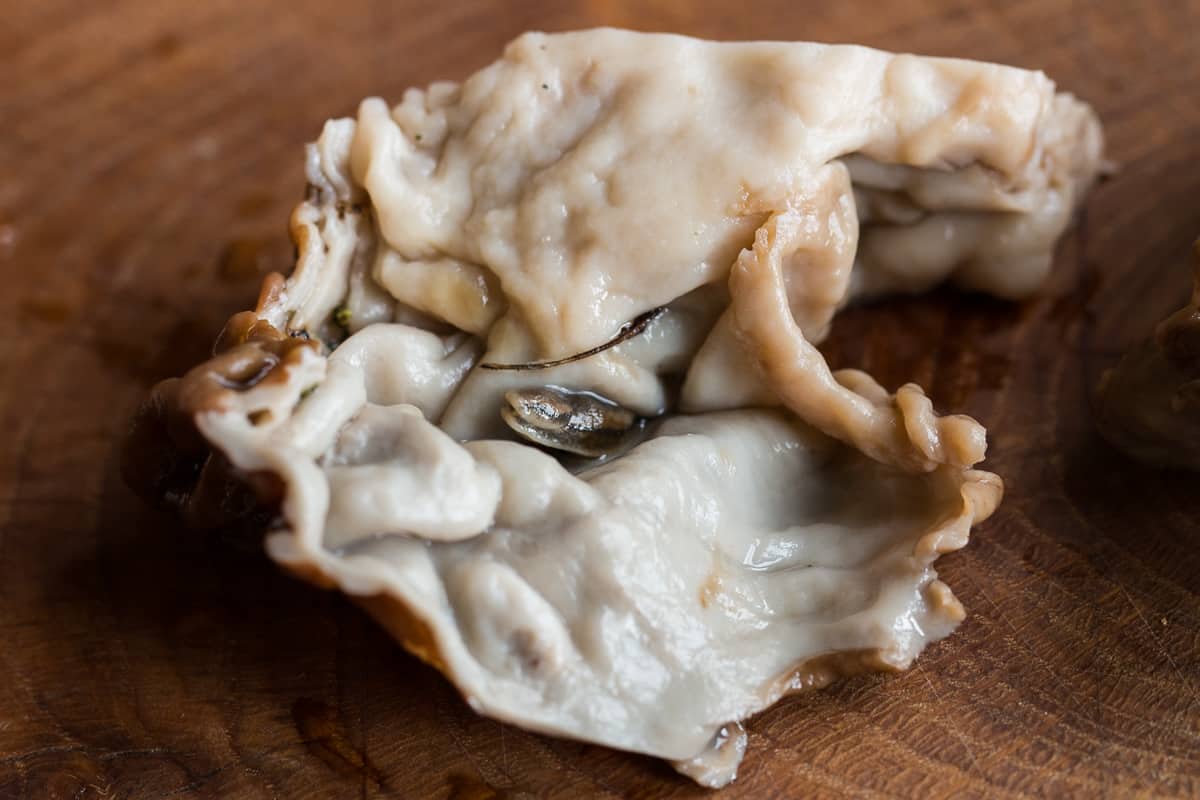



Cleaning
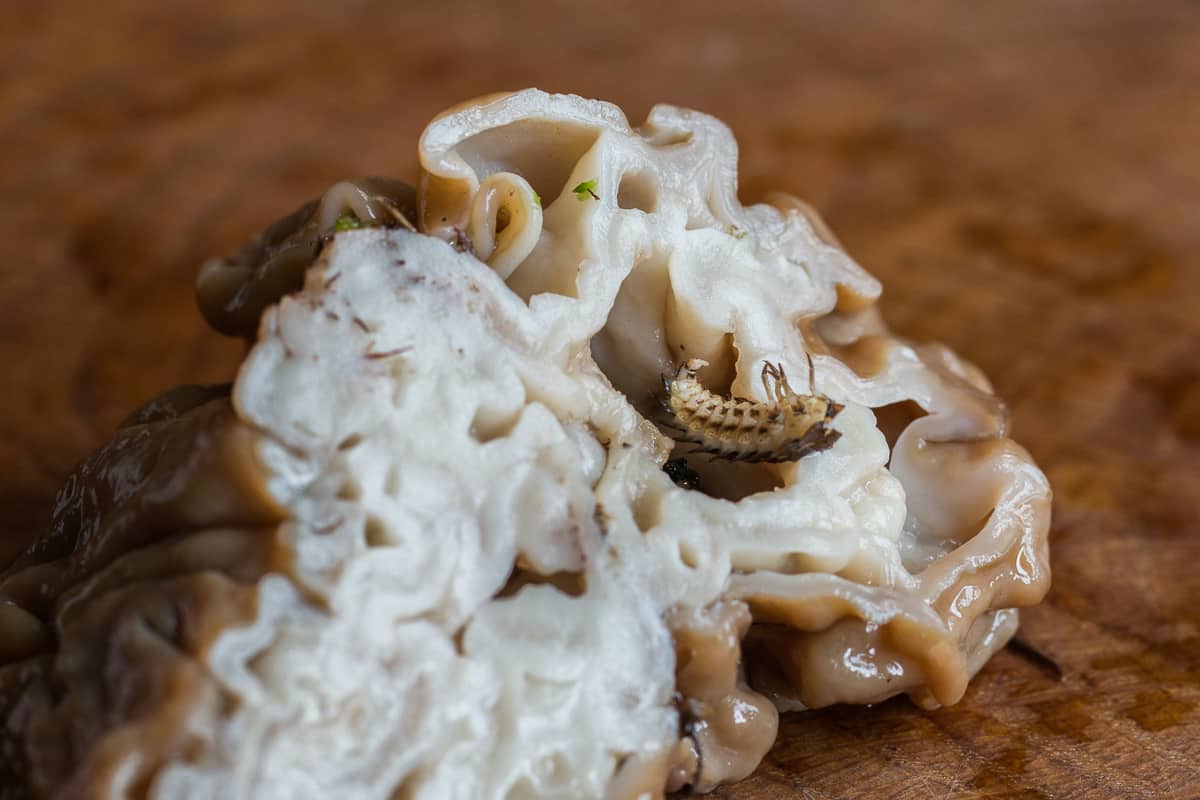
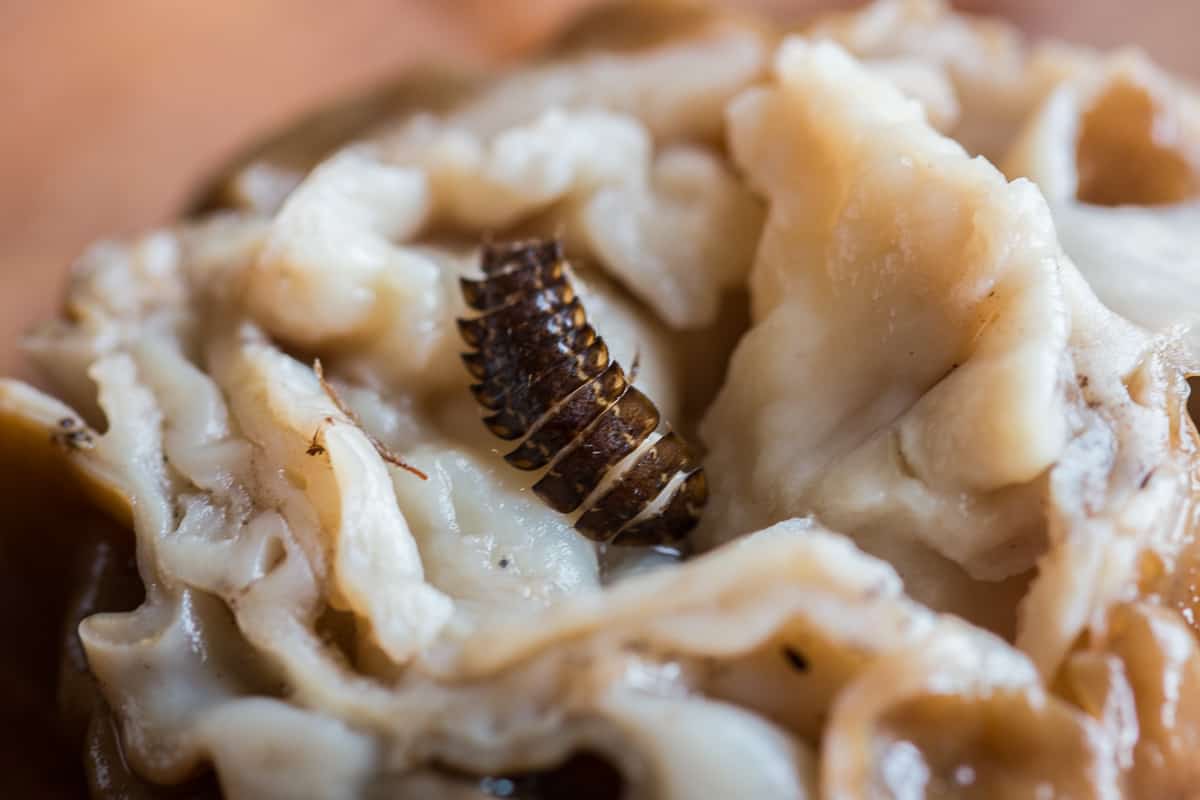
Knowing your species, etc, is only half the battle here. When it comes time to cook them, there's another learning curve---cleaning. Gyromitra korfii that I've eaten have lots of folds in their pileus and stem.
Those folds inside can also be infuriating to clean. Like hen of the woods they can function as shelters for bugs, and even in pristine mushrooms.
I regularly have to rinse and look over mushrooms after blanching to make sure there aren't any cooked slugs, sticks, dirt, or other debris. Yummy, right? After blanching, cut them in half or into large pieces depending on size and inspect them, then proceed from there.

However you feel about false morels, I hope this article has been at least a little helpful for you, and at the very least may help you to not kick them in the woods when you see them.
How to Cook False Morels or Gyromitra Mushrooms
Ingredients
- A few tablespoons of unsalted butter or cooking oil
- Gyromitra mushrooms
- water
Instructions
- Inspect the Gyromitra for bugs, debris, and dirt. Clean the mushroom diligently, swishing around in a bowl of cool water as needed to loosen any dirt. Cut it in half if small or quarter them if large and inspect diligently for bugs and debris.
- Open all the windows in your kitchen, and use a kitchen hood fan if available, or use a box fan to blow air out of the kitchen if you're cooking Gyromitra esculenta or others with higher amounts of gyromitrin. (See safety note)
- Bring a pot of water to a rolling boil, add the gyromitra, put a lid on the pot, bring it back to a rolling boil and cook for 10-15 minutes, depending on how many you're cooking, or until they're completely cooked and wilted.
- If using Gyromitra esculenta, repeat the process 1-2 more times.
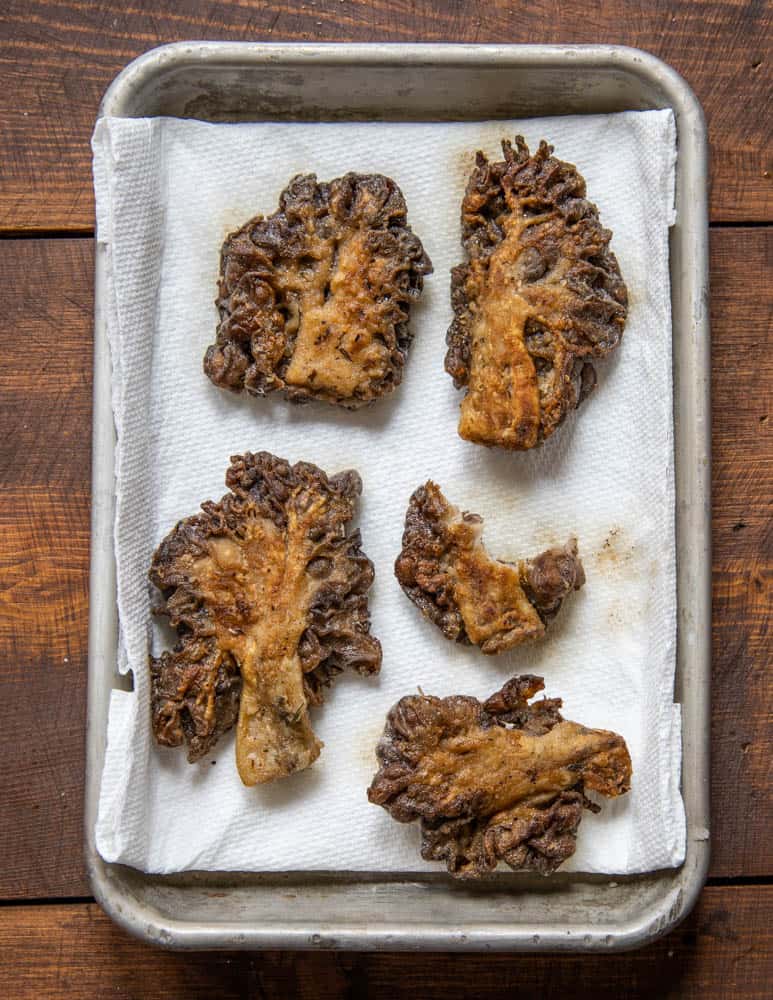
- Remove the Gyromitra. Discard the water. Put the Gyromitra between a few sheets of paper towels and press to get out as much water as possible. Season both sides of the mushrooms with salt.
- Heat the butter in a skillet, like cast iron, and cook the mushroom on medium low heat about, flipping once, for about 5 minutes on each side, or until the mushroom is deeply caramelized and browned, then drain for a moment or two on a paper towel to shed fat, and eat. Sprinkle some extra salt as you eat if you think it needs it.
Video
Notes
Some Gyromitra must be par-boiled before cooking, especially Gyromitra esculenta. Some, like G. caroliniana and G. korfii do not need to be boiled. If you do not boil them, the mushrooms must be well cooked for at least 15 minutes, and I recommend using a wet saute to ensure they're cooked. Ventilation I recommend using ventilation, fans, or a hood vent while par-boiling, but it's in the interest of being overly cautious. Gyromitra esculenta must be par boiled, as well as some others.

Further Resources and Reading on Gyromitra Edibility
Micheal Bueg, Phd: False Morels, an Age-old Question of Edibility
Various Authors: 30 Years of Mushroom Poisonings from the NAMA Registry
Tom Volk: Gyromitra/False Morels.


Papa Permaculture
Currently eating your recipe, ain't dead yet, it's delicious. Will report back in 24 hrs unless dead.
Alan Bergo
You'll be fine. I only eat them once in a while as a novelty. They're so easy to find it kind of takes away the fun.
Papa Permaculture
Well, it was delicious, and I'm still alive. We knew there's not much short-term risk involved, and looks like it's more of a long-term thing, if I understand correctly. Just wanted to try them, since the locals do, and to satisfy my curiosity. Thanks again for the recipe and entertaining article, Mr. Bergo.
-Sean
@papapermaculture
baly
be carefull!!! dont eat them anymore very hight risk of S.L.A(maladie de chacot)
Your future will dependon your level of vit A and it is no constent this means :at any time, you can get hill or not!!!
Alan Bergo
Gyromitra are a traditional food around the world, as I mention. Ethnobotanical and historical documentation of consumption strongly disagree with you.
qq
Do you really want us to BARE with you?
Alan Bergo
Thanks for letting me know, spellcheck is not an exact science. You might want to check your use of caps too.
Chris
I have eat the Carolinana variety since I was 5 years old I'm 30 years old now I've never pre-boiled the mushrooms how my family prepares them is by slicing them into rings put them in a bowl cover in salt water and soaking them overnight for at least 12 hours rinsing the water out and soaking in fresh water for another 6 hours then rinse and then flower them and deep fry them if they haven't been soaking long enough they will have a bitter taste but when properly rinsed and washed they'll actually taste better than morels to me and are more filling than morels and I've eaten whole plate full of them with no problems ever
Alan Bergo
Chris. Yes, eating G. caroliniana without par boiling is pretty well documented, but, because they need very thorough cooking, and because the species is still maligned and listed as poisonous is field guides, I do recommend people blanch them, unless they’re very comfortable with cooking them, as you are. I hope to try them someday.
Andrew Skorzewski
I found a few false morels growing on rotting logs last week, This is the first time I have seen them other than spring.
Alan Bergo
Do you mean Helvella?
Sheri
We have abundant g. montana in the high elevations of our mountains here in Utah. We also have g. esculenta. The g. montanas are excellent and do not require boiling. I would never bother with the g. esculentas since it's so easy to get the safer g. montanas. Delicious and far more abundant than morchella here if you can get high in the mountains where there is still snow in the spring.Yum!
Alan Bergo
Our local korfii is supposed to be similar to the montana. I find them to be quite good, not as good as morchella, but good when I'm coming up empty handed.
Shawna
Thanks for this! Found alot of korfii today and I am excited to try it! I will use your information as great guidlines for preparing them.
Alan Bergo
Try the gratin. https://foragerchef.com/gyromitra-gratinee/
Jessica Beaver
I'm trying my first false morel right now. I started cooking it before I read this and boiled them twice with a rinse in between but not a lot of water. Then simmered/fried them up. I think I cooked a lot of the flavor out of it lol, but I wanted to be safe. Now I know, thank you for the article.
Ryan LeClair
Very interesting article. I landscape, and one of my helpers pointed out a Gyromitra to me in the front yard of a random house, asking if it was a morel or not. It had a red cap, and I said it was likely a false morel. I came across this article in my attempt to verify that assertion, and I was shocked to find out that they are edible with proper preparation. I suspect the mushroom is G. Carolinia. After reading this article, I am half tempted to go back by that house, and snag a couple of those caps to try eating. Thanks for the great article!.
Alan Bergo
Thanks for taking the time to look through the article--I've tweaked it for years now whenever I find good info to add. The world has been so inundated with fear and misinformation regarding the Gyromitriaceae, it's time they got the credit as a historical food fungi they deserve.
Steve Palodichuk
As a Chef first.. And a foreger. Why would you even pick them . leave them in the woods!!!! My "patch" of morels. (6 lbs so far foreged.) And sold to local rerestaurants. And if you are currently eating on eat street or lyndale ave. You are eating my morels and oyster mushrooms. These chefs trust that I am bringing them the best wild mushrooms that Minnesota has to offer. Pleases don't play with the consumers health. And make a bad name us.
Alan Bergo
First of all, if you think I'm selling Gyromitra to restaurants, you obviously didn't read the post. Secondly, I don't give two shits if you sell mushrooms, or where you sell them too. It's people like you, that parrot and regurgitate outdated information that give foragers a bad name. I'm spreading knowledge, and asking people not to trust every single guide book (that also often regurtitate outdated information) to open their minds and not throw away the entire Gyromitra genus just because of Gyromitra esculenta, which, as I covered here, has been eaten for a very, very long time regardless, and will continue to be, whether we like it or not. People that eat G. esculenta need to be aware of the possible dangers, and people that spew anti-Gyromitra rhetoric need to get up to date with science.
Mary E McNaught Zeman
Didn't know they were supposed to be parboiled, we've always just saute'd them. We only take them when there is nothing else around worth taking as the texture isn't great. The ones we do pick in Oregon are a shade of lavender/grey and we call them "brain mushrooms". They may, in fact have a cumulative toxic effect; I wouldn't know as I have only eaten them for seventy years However, as I said, when the good stuff is out, "We don't pick'em, but we don't kick'em."
Alan Bergo
I'm happy to hear you've been enjoying Gyromitra for so long. The mushrooms you're describing sound different than Gyromitra esculenta, and, if you have any images, I'd love to share them in a group I'm in that specializes in Gyromitra identification and edibility. We would be able to tell you what the species is exactly.
Papa Permaculture
Would love to know the name of this Gyromitra group you mentioned, if it's still around. Thanks so much for the article and sources! I live in Belarus and just foraged a bagful of what I'm pretty sure are korfii, and am hesitating to try them. The locals do, after double par boiling... I probably will give them a try here in a few minutes. Hope I don't die!
Alan Bergo
If they double boil it's likely G. esculenta, but I'm guessing. I don't eat those. It's impossible to tell for sure without pictures, but G. esculenta looks very different from korfii, at least to me. G. esculenta is much darker red to purple where korfii are shades of tan as in my pictures.
Melanie Goforth
You are a joy ! I found a big korfii today and I am going to boil it twice and yes , enjoy eating it !❤️
Alan Bergo
Tis the season.
Amber olmos
Would you happen to know of any, updated, or recent, mushroom guide books?
Alan Bergo
100 Edible Mushrooms by Kuo is a great book, for starters.
lisa
He's got a more recent one, Mushrooms of the Midwest, published 2014.
Alan Bergo
Thanks Lisa
Julia
Great article! I'm originally from Russia and I remember as a child we have collected both Gyromitra and Morchella mushrooms together as a family and cooked them together. I was little, so I don't remember if my grandparents cooked them differently, but we ate them all and no poisoning ever occurred. I'm in North America now, and I forgot about them until I saw a few in the forest and started reading about mushrooms again. I guess it also depends on traditions, and people in North America are more cautious for some reason. Lots of misinformation too. I know people, who still live in Russia, have been collecting Gyromitra esculenta for years and cooked them and ate them and still alive and in good health. They do, however boil them twice, 10 - 15 minutes each time, changing water in between, and them fry in butter. Delicious early spring mushroom. There was a question why bother when you can have Morels. But these sometimes appear before Morels and we all miss mushrooms so much through the winter.
Not suggesting anyone to risk it, but like Alan said, people will try either way.
Thank you!
Mitch
Just to note - the only species that are known to contain gyromitrin are G. esculenta, G. infula and G. ambigua. Other species “may” have it, but certain species such as G. brunnea; G. caroliniana; G. korfii; G. montana ; G. gigas; G. sphaerospora; & G. fastigiata have either never tested positive for the toxin, or simply have not been tested, as far as I know & can find.
I have been told (and have read) that G. brunnea does not contain gyromitrin, and tastes delicious, But, do your own research, send in mushrooms to get tested yourself if you have the means, & come to your own conclusions.
It would be great to clear this up, species by species, once & for all. It would be a shame to pass up choice edibles just because of a few species & general fear if there is no need to.
Great article as always.
Alan Bergo
Wow, thats some great info Mitch, thanks for contributing.
Rachel
Thinking about trying my first false morel ! I find them all the time while driving in south Saint Louis and always standing alone big red ones
Dave
Why bother rolling the dice on this when I find more morels than I can eat virtually every spring? I've eaten 16 different species of edible mushrooms that I have foraged in MO. There are far too many safe mushrooms to fodage and eat to bother gambling with health or life.
Alan Bergo
Thanks for commenting Dave, I completely agree people shouldn't eat Verpa or Gyromitra. Do you have documentation or a link to an article about people dying from pressure cooking morels? I'd be very interested to read that.
David Arora
Toxicology of Verpa is same as for Morchella.
Alan Bergo
Would you want to elaborate on what that would mean for someone who might eat a verpa thinking it's a morel, or interested in doing so? Thanks for your comment, I loved seeing your adventures in Africa via FB.The termite mushrooms in houses and the "Ten tente al dente" were really great.
Tiitta Tatti
Another Finnish commenter here. I'm mostly chiming in to emphasise the importance of what Manse Mies already said.
Gyromitra esculenta are extremely common in Finland, and during spring season you can see them being sold in marketplaces and even supermarkets with warnings similar to this: https://i.imgur.com/0ARmPct.jpg
They're delicious, and make for a particularly great soup. They're also very abundant, and you can often bring back home dozens of kilograms if you find a good spot.
But obviously, they're extremely dangerous. When eaten raw, they can easily be lethal, and even if you don't notice any symptoms, you still aren't in the safe: the toxins will pile up in your body and cause trouble down the line. At the very least kidney damage, at worst, cancer.
All poison in the mushroom is water soluble, though, which is why boiling is as effective as it is. A single parboil should remove about 99% of the poison, rendering it mostly harmless. But to be on the genuinely safe side, ESPECIALLY if you plan to eat them more than just one or two times, you need to parboil them twice.
As Manse Mies said: Parboil once for 5 mins, toss water away, replace it, parboil again for 5 mins, and only then eat. Only that way you'll get rid of the last 1% of the bad stuff remaining. (Given how popular the mushroom is in Finland, there's plenty of research about the subject: it's SAFE to eat this way, if you just do it properly).
Manse Mies
The Finnish Food and Health agency suhgests that the Gyromitra should be parboiled two times, 5 minutes each, changing the water in the between. However, that might not be true for all of the Gyromitra species in the states, as some of them may contain larger amounts of the toxin. A very tasty spring mushroom though, and a very sought after and expensive thing indeed. If you ever visit Finland in the Spring, try the False Morel soups and the stews, they are exquicite.
Alan Bergo
Great information, thanks for sharing!
Jacqui
Do you know anything about Helvella crispa? I think it is a very similar phenomenon. I was introduced to these by friends who pick and consume them regularly and I was surprised to learn that they are considered toxic (after having eaten them several times and fed them to friends... oops) because they apparently contain monomethylhydrazine. Of course the cancer risk is a rather long term problem - not like having your liver dissolved within a couple of days - so who knows, perhaps the seeds of disaster have already been planted and I'll find out in 20 years. There are worse fates.
Do people eat Helvella crispa is North America? Some people do in France, at least.
Alan Bergo
I do know a bit about them, and I know a number of people that eat them in the U.S., specifically out in Montana, especially the black variety that I don't see here in MN.
brian wadyka
I've never had H. crispa, but we have tons of Helvella lacunosa here where I hunt in western Oregon. I've been eating it for years. I always dehydrate it first, then use in stir frys or soups.
Doug
Thanks for the article. I enjoyed it completely. In southern Missouri and Illinois we have been eating these for decades without problems. I don't think that Michigan is alone in it's addiction. They do tase wonderful, but everyone I know down here doesn't boil them. I have personally never met a individual that has had a problem with them. I know what they say but I know alot of mushroom hunters and they are all healthy and alive. Thanks again Doug
Alan Bergo
Thanks Doug. I know lots of people like to eat Gyromitra, and I'd be lying through my teeth if I said it was anything but delicious. That being said, I would get seriously witch hunted if I suggested people eat them, so I err on the side of suggesting caution. This was one of the more interesting cultural/mushroom research projects I've done. Fun to hear about you enjoying them down in Missouri and Illinois, I hope someday we know more about them so we can pick out species that don't pose any sort of health issues, so more people can enjoy the safe species of these interesting mushrooms.
Jeane
Wish there was a chemical test developed you could do to see the levels of toxicity of this type of mushroom.
Alan Bergo
I know.
Fred Terracina
The second author is Mitchell the correct title is closer to Toxic and Hallucinogenic Mushroom Poisons.
Fred Terracina
Although I am aware that par boiling A . muscaria is done by some, I do not think you should in any way encourage this practise. There are likely to be some foragers who fwill thinkthat parboiling other species of Amanita and other genera and species of "toxic" fungi will destroy all the toxins they contain. This is a false and dangerous assumption. I suggest you reread Lincoff's (and another author whose name escapea me) book on Toxic and Hallucinogenic Mushrooms.
Alan Bergo
Thanks for your thoughts on this. I don't suggest people eat/boil/fry/bake or consume muscaria in any way, but I think people will try with or without my saying anything on the subject. On a tangeant, In Minnesota, muscaria are dried and sold in Wicca stores under the counter as a very lucrative narcotic business (which I unfortunately used to contribute to, in all honesty). I don't condone their consumption in any way there are much better mushrooms to eat.
James
Ive eaten mascaria. It is one of the best mushrooms ive ever had. All the toxins boil off of it. Ypu just have to discard the water. Plus all the toxins of that mushroom will do to you is make you puke and go to sleep or maybe have an hallucination. But i wouldnt recommend it to someone not willing to take a risk. Lol
Alan Bergo
Yeah I've eaten it too, it's not too bad. I did a podcast (there's a link on the press page) with a guy that ate muscaria raw. No thanks.
falsemorelchomper9000
Just an FYI whereas boiling amanita muscaria very hot and long it in huge pots of water and dumping the water repeatedly removes all the ibotenic acid and muscimol, simmering it at exactly 190 degrees in exactly ph 2.7 water (typically via citric acid) for exactly 3 hours converts most of the ibotenic acid to muscimol getting rid of most of the nausea and alcohol like effects and leaving only the psychoactive effects). It's an interesting experience when you're not nauseated and unable to walk. I guess historically people would have animals or a shaman eat them and take on the sickness, where their bodies would convert to muscimol and pass through to the urine, where they would drink the urine and experience the effects without the negative effects of the ibotenic acid. Poor shaman... all of the negative effects with none of the party urine.
In any case I definitely prefer them boiled for food, but it is an interesting experience.
Alan Bergo
Interesting. Poor shamans indeed.
Martti
Dear Fred. I am 78 years old. I was born and raised in Finland. I have been living in Canada since 1964. As a child growing up in Finland I used to pick mushrooms with my family. Gyromitra Esculenta was and is still one of the most sought after fungi in Finland. I have also pick them in Alberta Canada. According to my Finnish knowledge and to prepare them for consumption I split,cut and cook them in boiling water for 10 minutes- twice.
They are delicious however I do limit my consumption to half of dozen time's in a year due to the accumulative effects of the toxins. I now live in British Columbia where fungi are plentiful.
Best Regards
Martti
Alan Bergo
Thanks for commenting Martti. I was in Helsinki picking chanterelles last year. Had my first sauna too.
Katie Goin
Hi Alan, Found a bunch of these crazy looking false morels in a spruce forest. I think I will refrain from eating them out of fear! But a fun find to see mushrooms! Wondering if you have done more cooking with them since this posting ?