Fiddlehead ferns are a harbinger of Spring, and, along with ramps and morels they're some of the most widely known and desired spring edibles I look forward to eating every year.
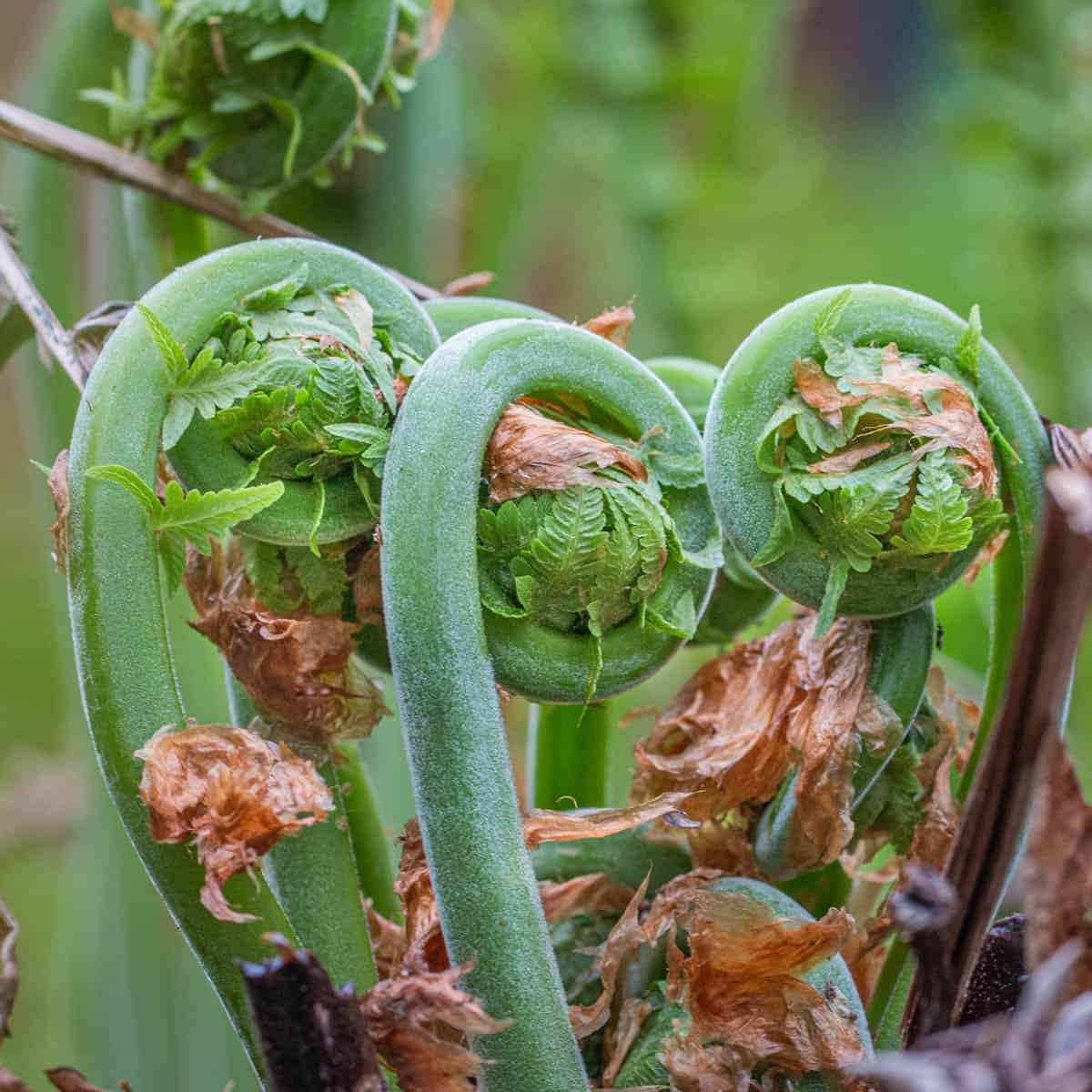

There's a lot of misinformation and confusion about fiddles, so I'm going to give you a deep dive here and explain how to tell different species apart and find fiddleheads that won't make you sick (it's not complicated) as well as show you how I cook and preserve them.
Habitat
Fiddleheads seem to be pretty much any where I go in the spring with woodsy trails, but my best spots are in areas near water with rich soil and a decent amount of shade. Look for hardwood forests with rich soil, preferably near a river, creek or stream.
 Different Species
Different Species
There's a couple different fiddleheads you can eat (2 or 3 depending on who you ask). Since I hunt in the Midwest most of the time, I'm referring here specifically ostrich ferns or Matteuccia struthiopteris, since I think they're probably the best for the table and they grow near me. Edible Fiddleheads from the West Coast are usually lady ferns (Athyrium filix-femina, a slightly different species that, while still edible, I don't like quite as much as ostrich ferns, but are still great to eat.
Ostrich Fern (Matteuccia struthiopteris)
The typical variety I harvest in the Midwest, and the one most people will know.
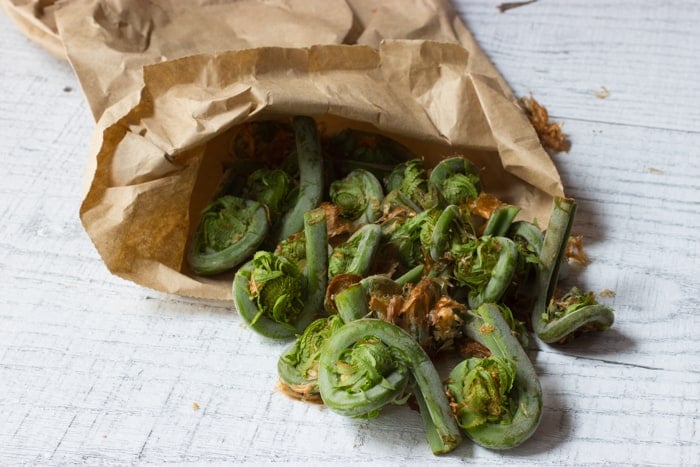

Lady Fern (Athyrium filix-femina)
The West coast variety. Lady ferns are the fiddleheads I see most commonly available to restaurants through wholesalers, which means they can show up on store shelves across the country. This can confuse some people when they look for edible ferns in places where the lady fern doesn't grow, since their appearance, at least to me, could more easily be mistaken for an ostrich fern look-a-like.
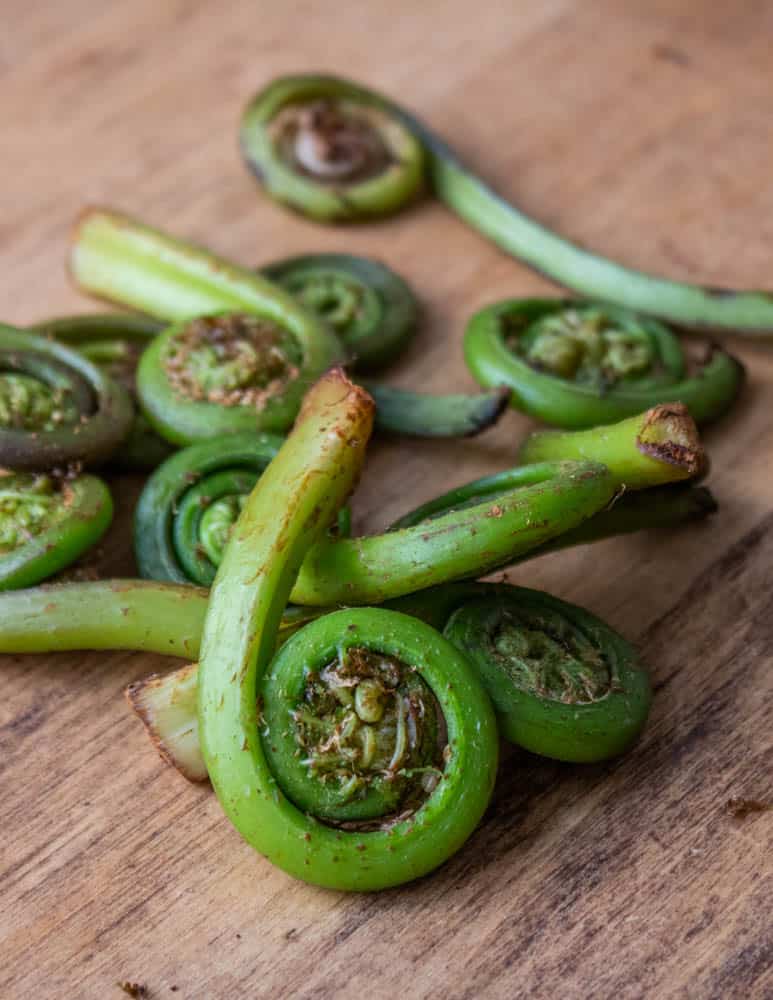

The U shape of the stem
One of the most important and easy ID features of ostrich ferns are their stems. The stems have a tell-tale "U" shape to them, where other ferns that might make you sick have solid stems. If your fern doesn't have a stem as in my picture below, it isn't an ostrich fern.

Harvesting and ID Tips
1. The ferns should still be tightly coiled, you do not want to pick or eat any that are totally unfurled.
2. Ostrich ferns will have a "u" shaped stem it will not be round/solid--ever
3. The ferns will have a brown papery covering on it when young, not white, which should be be removed before consuming. White coating on your ferns means you have a different species, typically something like Osmunda, or the interrupted fern--don't eat or serve those to others as they can make you sick.
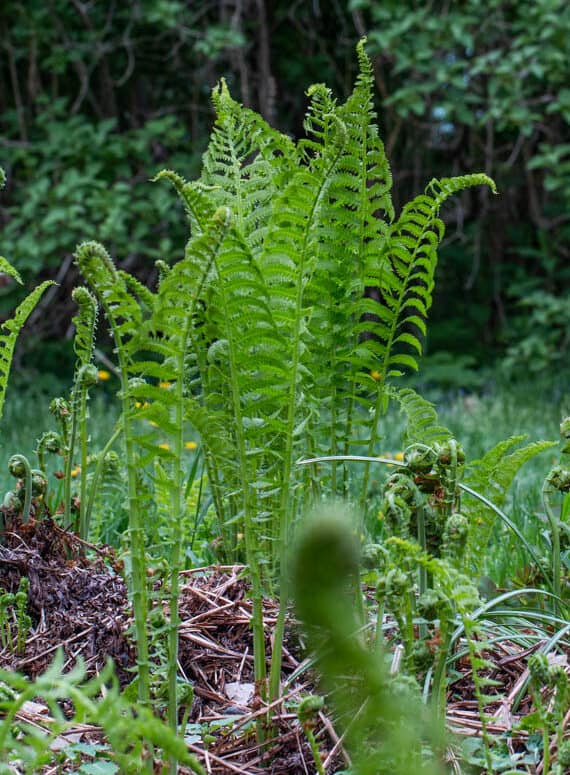

Sustainability
Since they're so popular, fiddleheads are commonly overharvested. If you harvest your own, and especially if you harvest from public land, know that it's considered bad form to take every fern growing from a fiddlehead crown. Take a couple fiddles from a crown, and move along. Think of your harvesting as "thinning" the ferns from a plant, as opposed to clear-cutting, which some do.
Growing your own
Ostrich ferns make great "edimentals" or edible ornamental plants. They'll come back year after year, and you'll be able to harvest fiddles without leaving your driveway. Contact your local garden store or ask a friend for crowns.
Finding your patch for future harvests
Fiddleheads and other ferns are fascinating in how they reproduce. Most of the plants that grow near fiddleheads will reproduce by making flowers that produce seeds after being pollinated, fiddles are different. Similar to mushrooms, fiddleheads reproduce by creating a stalk that produces spores. This is the brown stalk that looks a bit like a bird feather below, and noticing them will help you find patches of fiddleheads during the off-season.
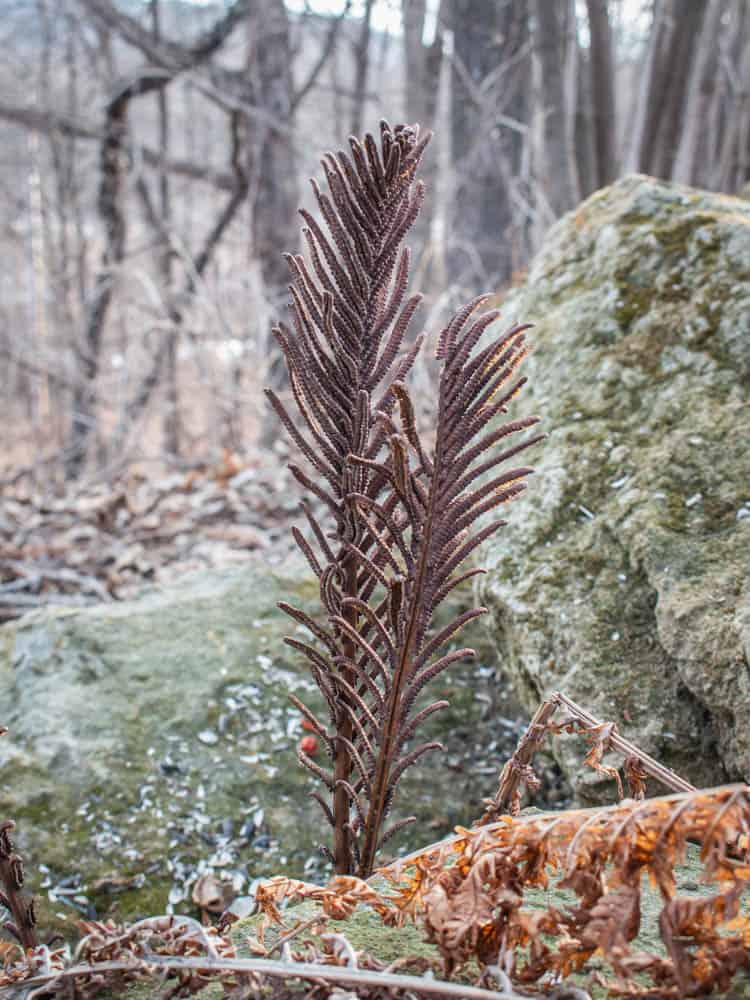

Cooking
Don't eat them raw
No matter what species of fiddlehead you have (as long as it's one of the two I've mentioned) they need to be cooked and should not be eaten raw. Despite the claims of some people that they can eat them raw without an issue, most people can't, and if you feed someone fiddleheads for the first time and they get sick, you're likely to scare them away from fiddleheads, and potentially wild food in general. That being said, there's definitely a sweet spot for cooking, as overcooked fiddleheads are mushy and unappealing.
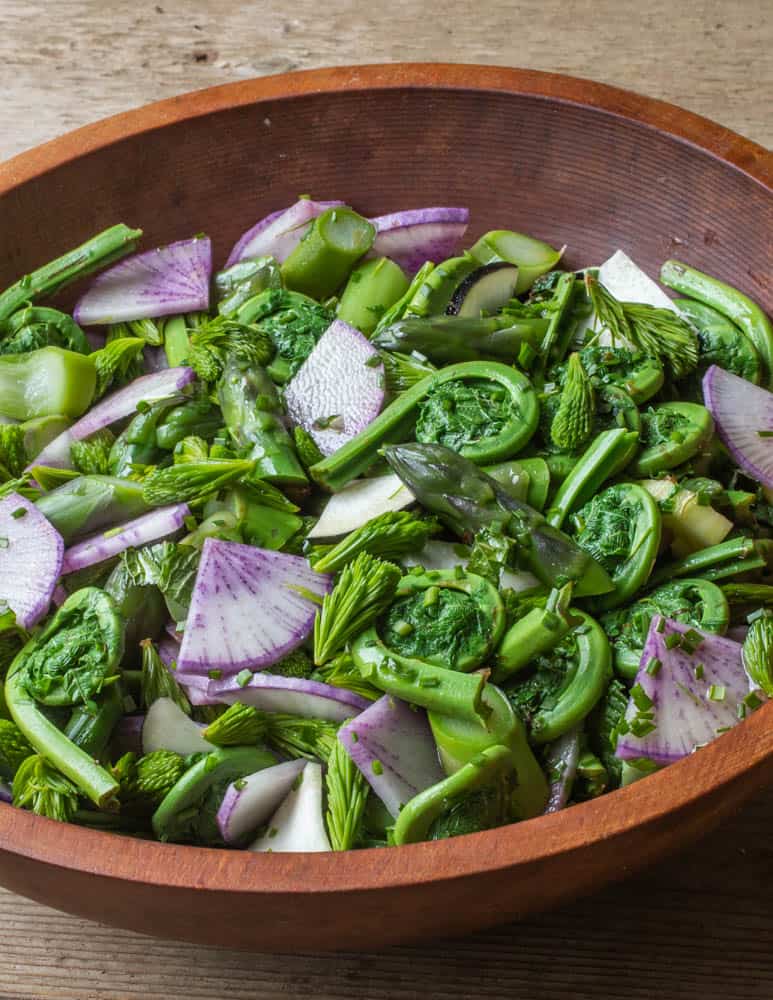

Blanching
The tried and true method for cooking fiddleheads is blanching. Although you can cook fiddleheads by simply putting them in a pan, it's not ideal as it's easy to overcook them, have them soak up too much oil, or turn black in spots from uneven heat.
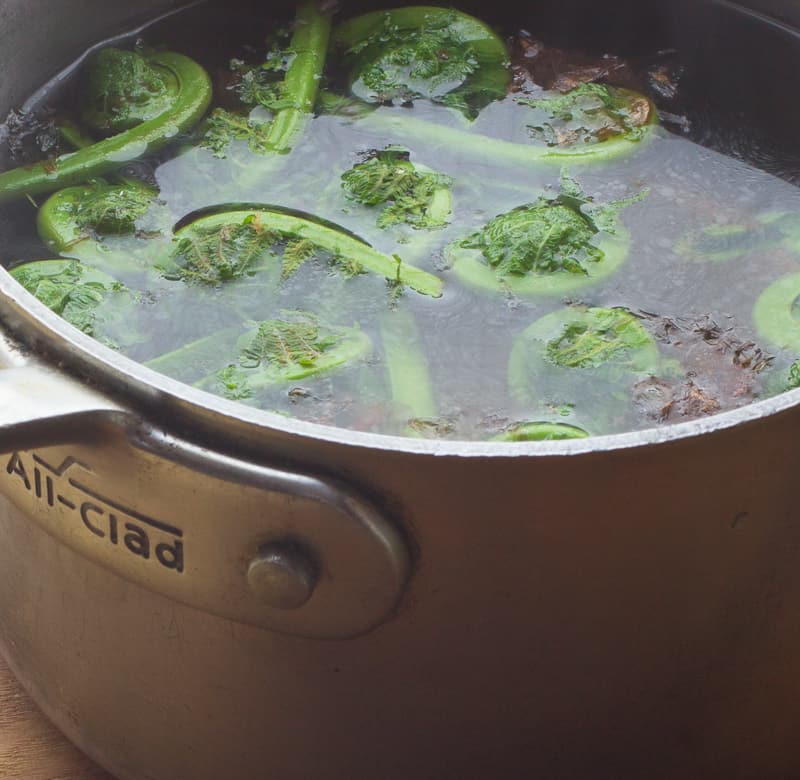

To blanch fiddleheads, put them in boiling, salted water for 1-2 minutes, then remove and allow to cool without putting them in an ice bath, which can cause them to discolor. Blanching locks in and preserves the green color, as well as par cooking them a bit so they don't discolor and oxidize (turn brown) after cooking, which, while still being edible, is unappealing.
After they're blanched, fiddleheads can be added to all kinds of things: salads, soups and stews to name a few, but do make sure not to cook them too long as you want them to be a little crisp. Fiddleheads should not be mushy.
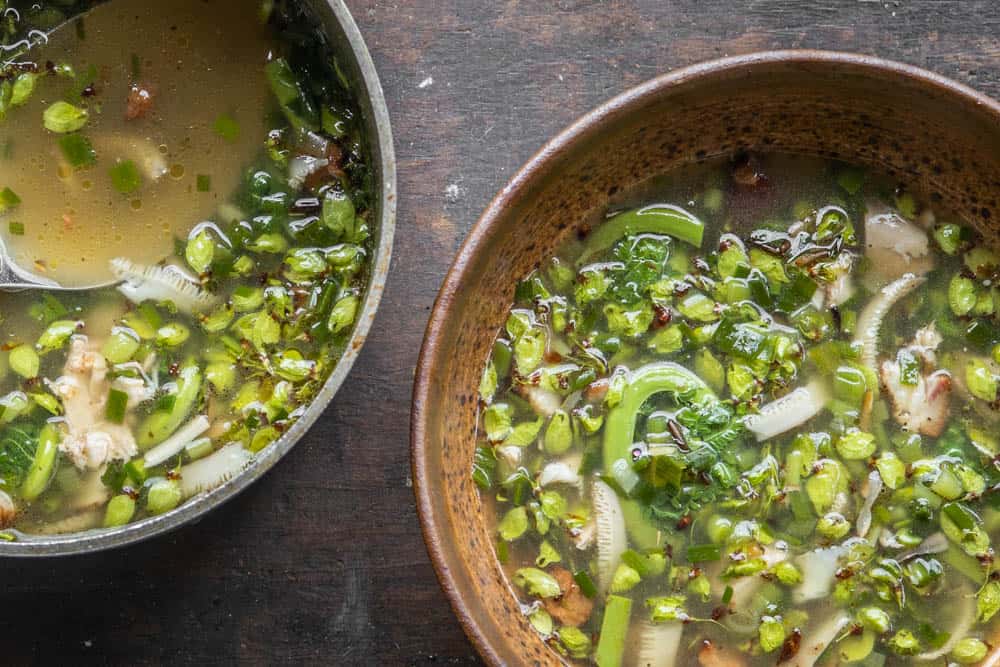

Preservation
There's a few different ways that you can preserve fiddleheads for use in the off-season, and some are better than others. here's a quick list.
Dried
Fiddleheads, specifically bracken fern (known as gosari) are dehydrated, and are an integral part of the Korean dish Bibimbap, a sort of meal-in-a-bowl consisting of rice, eggs, various vegetables and condiments. To dry fiddleheads, I blanch them, and then dehydrate, which helps them keep their color.
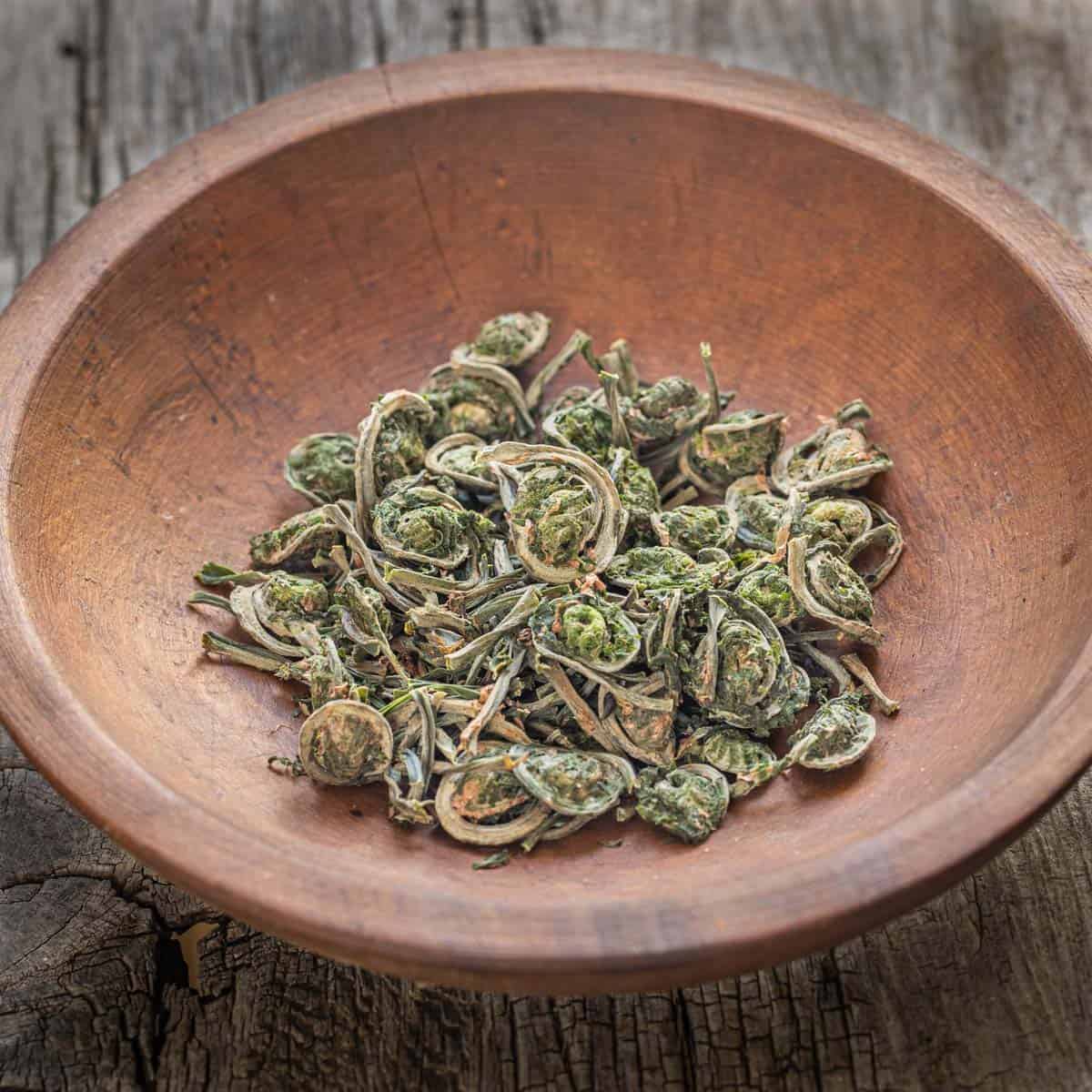

Commercially dried bracken ferns are discolored as they're dried from fresh, as opposed to being blanched. I suspect blanching also reduces some of the potentially problematic compounds found in bracken fern, but I'm speculating there. Either way, blanching fiddles before drying improves them. See more on drying and cooking with dried fiddleheads in my post on them here.
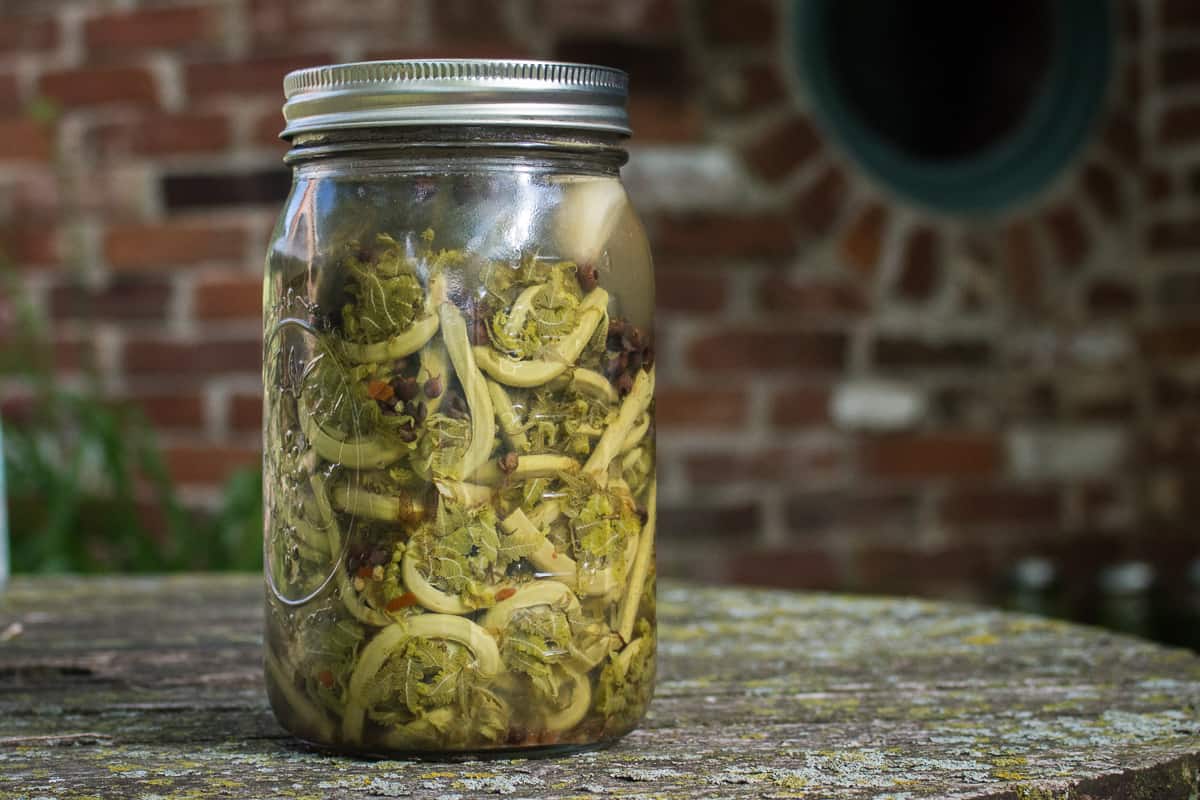
Pickled
Pickling works well with fiddleheads as it can keep them crunchy. That being said, in order for them to keep their tender-crisp texture, you'll need to follow my recipe for crunchy pickled fiddleheads, as canning in a waterbath will make them soft. See a recipe for pickling fiddleheads here.

Freezing (not recommended)
Some people claim to have success freezing fiddleheads, but just because it can be frozen, doesn't mean it's going to taste good after it's thawed. Frozen fiddleheads develop a soft, mushy texture and I don't reccomend them. Better to eat them en-masse when they're perfect and in-season. Freeze drying is likely a great option, but I don't have one yet.
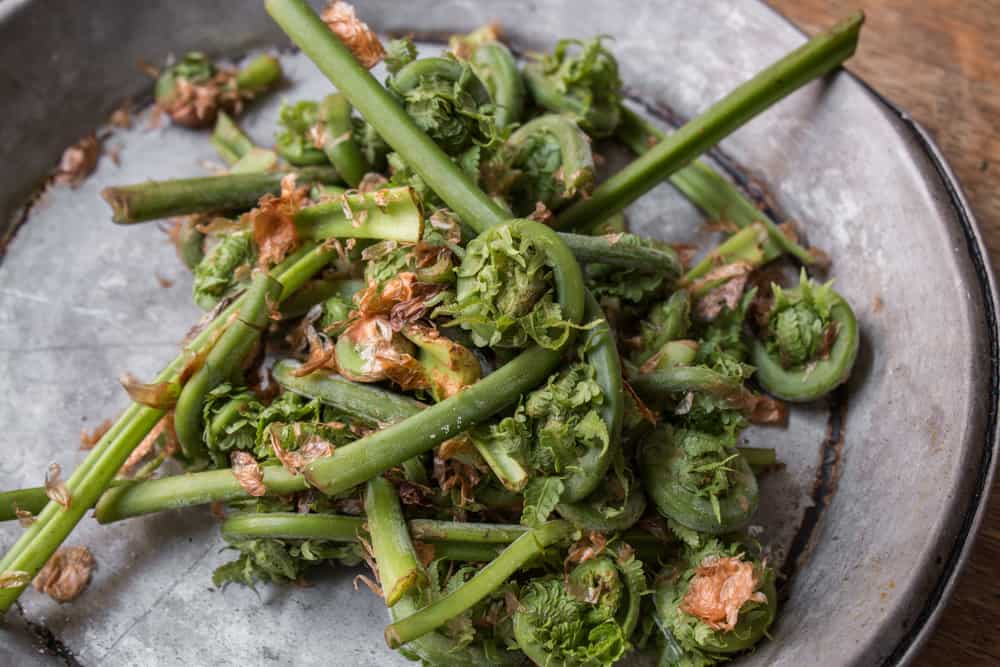
Don't throw the stems out!
Most people just want the curled crosier of the fiddle fern. But, as long as the fiddlehead is in a good stage for eating, the whole thing, long stem and all is edible, and you shouldn't throw it away after you trim them. Chop up excess stem, blanch and add it to a veggie sauté.

Overcooking
This is the most common problem with cooking these I see. Some people really don't like fiddleheads, and after having them prepared by someone else for me a few different times, I can understand why. Part of the problem is that people don't understand how they should be cooked, it's not their fault, fiddles are an obscure vegetable, and take skill to prepare well. When fiddles are overcooked, they're soggy, limp and disgusting. Sauteed for too long their heavy and oily. Cook your fiddles, but don't murder them.
Are fiddleheads poisonous?
There's lots of rumors and here say that either some fiddleheads are poisonous, only poisonous in some areas, or that certain species are poisonous. The problem, according to a number of foraging authorities, Sam Thayer being just one, is that many people, even moderately experienced foragers, identify the wrong type of fiddlehead, and eat them.
After they get sick, they spread the word that fiddleheads are poisonous, and then they tell their friends, and their friends tell their friends. It's like an unfortunate telephone game that slanders ostrich ferns and lady ferns, which, barring some individual sensitivity, are always edible.
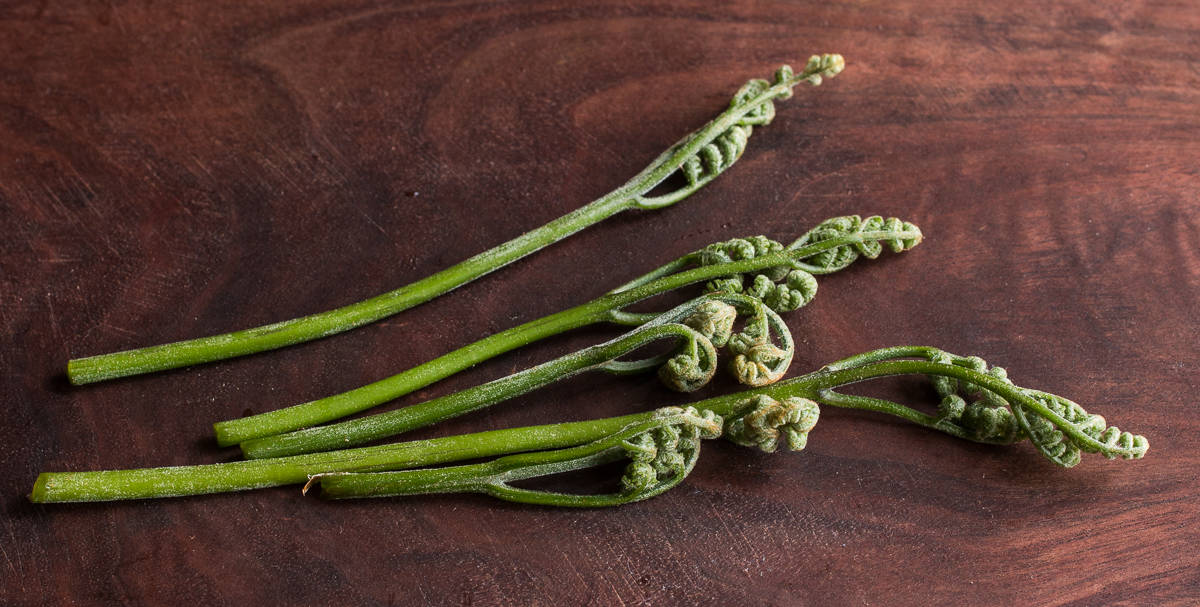

Bracken Ferns
Bracken Fern or Pteridium aquilinum (see picture above) is another species of edible fern that grows in my area, and around the country. Long eaten in the Far East, especially in Korea, these are one of the components of the traditional dish Bibimbap, and are widely consumed and sold dried in Asian markets across the United States--just look for bags of things that have the words "fern bracken" on them.
But, there's also information out there that says bracken ferns are cancerous, and shouldn't be eaten. I know plenty of people who eat these ferns after cooking, and are fine, but they also aren't eating them every single day, in large amounts. Like a lot of things, dosage is important, and we technically eat alot of things that could be "linked" to cancer. Ethnobotanical evidence, like with a lot of wild foods, is a useful tool. If I could find more bracken ferns, I would probably be eating them.
Bracket fern rhizomes
Bracken fern rhizomes are a traditional food of indigenous peoples of British Colombia and along the West Coast. The rhizomes were dug up and processed into a sort of "flour" then made into patties and baked on hot stones. I've heard the process of extracting the flour is difficult, and the type of fern used to make the flour has a much larger rhizome compared to the bracken ferns near me, which are small. Either way it's an interesting, well-documented example of ferns being used as a food. See below.

Basic Blanching Technique
Below is my tried and true, basic blanching technique I used in my restaurants. After blanching, the fiddles can be used for all-purpose cooking as you would other vegetables, or eaten raw, as in my favorite fiddle fern salad.
Blanched Fiddleheads
Ingredients
- Salt
- Water
- Fiddlehead ferns cleaned and trimmed, an inch or two of stem remaining
Instructions
- Bring some water to a boil in a large pot, add the salt until the water tastes "like the sea" (roughly 1-2 tablespoons per quart). Make sure there is at least twice as much boiling water as there is fiddleheads.
- While it might be tempting, don't omit the salt. Salt seasons the vegeatables and makes them taste better, but it also extends their shelf life in the fridge, just in case you forget about them for a day or two.
- Add the fiddleheads and cook until tender, about 2 minutes. If you want your fiddleheads more well done you can cook them a little longer, but if you cook them too long, they will get mushy. In your kitchen you make the rules, so make sure they taste good to you.
- Remove the fiddles and drain, then allow to cool naturally, there is no need to shock them in ice water to keep their color-if you do, they could oxidize and turn dark.
- Blot the fiddles with a paper towel to remove any excess moisture, then store in a sealed container or bag in the fridge until you need them. From here they can be cooked as you would any other vegetable, or seasoned and eaten in a salad, etc. They will last for 3-4 days in the fridge.
 Different Species
Different Species 
Renee West
Funny because when I lived in Madison, my yard grew literally hundreds and hundreds of Ostrich ferns (big yard) to the point of needing to pull some. . I did eat the fiddleheads and even started to dig and sell the ferns themselves to people to grow in their own yards because I had so many and they spread like crazy. The ferns absolutely loved my soil because it was rich black loam. I probably ended up selling a few hundred of the ferns over the time I lived there (I tried to tell everyone they could eat the fiddleheads, not many were interested) and I still had way too many in the yard. Those were the days.
Elisa
Out on a foraging walk in NY right now. Thanks for the clear info and pics!
Alan Bergo
You’re welcome.
tarah
Thank you for this great information.
You mention not having to ice shock them after blanching so I am curious what roll the ice plays in your list of ingredients.
Thank you again. I've been enjoying fiddleheads for years. It's nice to read more information and with ethical practices in foraging.
Alan Bergo
Thanks Tara. I used to blanch and shock fiddles, but once I read K-Jenji Lopez-Alt’s book I tried not shocking them and it worked well, and didn’t cause the ferns to oxidize and discolor after cooling. I updated it a few years ago and it looks like I left the ice in! Thanks for catching that.
Heidi
Everything I read says to boil them for at least 10-15 minutes to remove toxins that may cause food poisoning like effects. Do you ever experience this after only blanching for 1-2 minutes? Thanks for the info!
Alan Bergo
I've never had a problem at all, and I've probably served ostrich ferns and lady ferns to a few thousand people. Just don't serve them to people raw. As I mention in the article, there's a lot of misinformation about ferns online. For example, someone could harvest cinnamon ferns, which you shouldn't eat, get sick cooking them quickly, and decide to boil them to death. After they're boiled, the person might not get sick, and then they assume that cooking fiddleheads requires long-cooking, which they don't, but they pass on their experience of cooking an inedible fern as a true fiddlehead to others. That being said, if you try my quick blanching and want them more tender, cook them a little longer. You should cook things until they taste good to you. The only thing you don't want to do is overcook them so they get mushy. Also good to mention I’m not referring to Bracken ferns, as I don’t have as much experience with them.
Hannah
Thank you for this article. I live in Wisconsin and have been playing with the idea of fiddleheads for a few years, still haven’t tried them. I think this Spring will have to be the year! What is your best method for preparing them after you blanch them? Do you give them a quick stir fry or toss them in a salad!
Alan Bergo
After blanching them they can be used many different ways. One of my favs is a warm salad with lemon and olive oil.
Janet Kaye
We steam ours. They aren't cooking in the water. We find they have a better texture and more flavour.
Alan Bergo
Steaming can be good too.
Richard
In Alaska we batter and fry fiddleheads. Delicious!